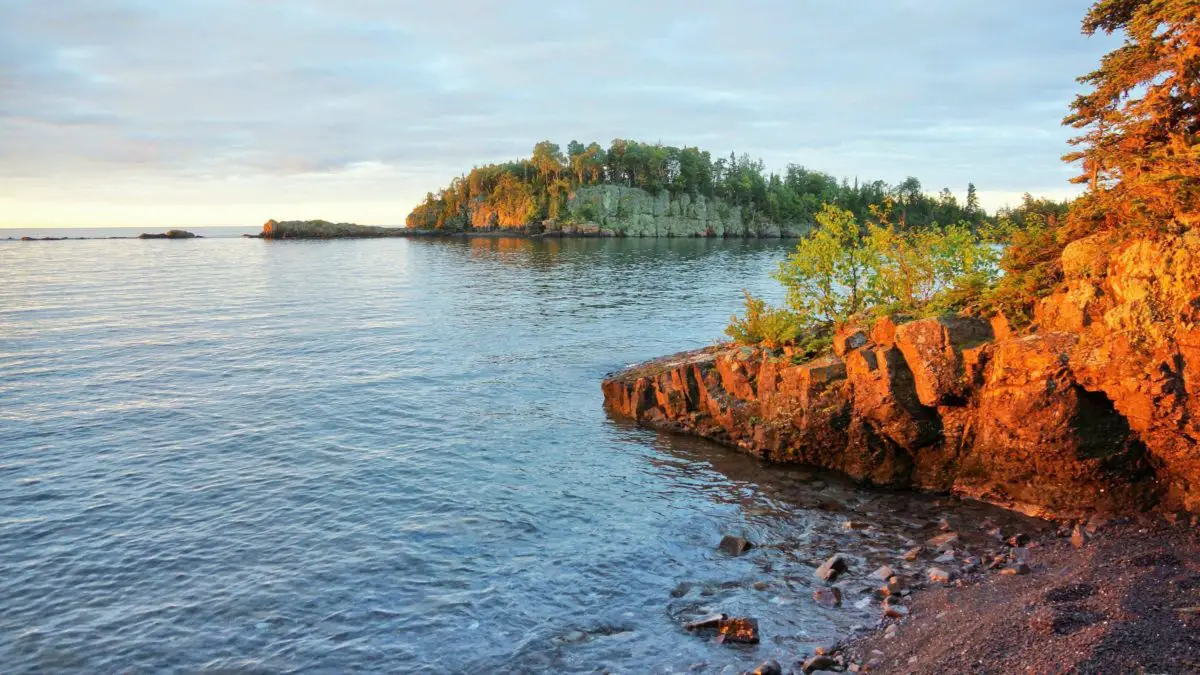Last Updated on September 2, 2023 by Hernan Gimenez
Lake Superior is the largest lake in North America, shared by the United States and Canada, and is considered one of the most important freshwater reservoirs in the world. Find out all about its history, characteristics, flora, fauna, geology and more in this article.
Indice De Contenido
History of Lake Superior
Lake Superior has historical antecedents that date back to the time when the ancient Ojibwe tribes of North American origin baptised it with the name “Gichigami”, which translated into Spanish means “Big Water”, a name worthy of the size of this lake.
However, as with many other places, the arrival of the missionaries during the colonial period led to the changing of certain names, and so it was with this lake, which was then identified as “Lac Tracy”, which can be translated in Spanish as “Lake Superior”, and which for the English becomes Lake Superior, while the French call it Le-Lac Superieur.
In reality, it is not the name that is important, but what it represents, especially for the regions that benefit from the presence of this lake in their territory.
Anthropological records suggest that the first people to settle in the Lake Superior area arrived as early as 10,000 years ago, when the glaciers retreated during the Ice Age. Remains found there indicate that they were caribou hunters, who also used spearheads to attack the animals.
Much of the evidence for these ancient civilisations has been found in regions such as the west coast of Canada, and they have been linked as the ancestors of the Ojibwa tribe, also known as the Chippewa, one of the largest indigenous peoples in North America.
These tribes settled around Sault St. Marie, specifically near Lake Superior, and lived there for over 500 years. By the 18th century, they were the inhabitants of the shores of this great lake.
How did this lake form?
It is interesting to know how Lake Superior was formed because its rocks are as primitive as the history of the Earth itself. Geological studies have shown that during the Precambrian period, more than 540 million years ago, magma rose and, on its way to the surface, formed granite within the Canadian Shield, the rocks that were not covered by the sea.
This was followed by a layer of basalt, which, due to the continuous flow of lava for over twenty-two million years, is up to 16 kilometres thick, causing the land to sink under its weight. This created the basin of the great lake we know as Lake Superior, which is very wide and deep.
Time and years continued to play a role in the evolution of these areas, where sedimentary layers were deposited, those already present were compacted, limestone, shale, taconite and dolomite were formed.
Many of these areas have been shaped by the advance and retreat of the glaciers during the great snowfalls which, when they melted, created shallow seas which, especially in the south-eastern part of the lake basin, caused floods and deposited sandstone and water.
Lake Minong, considered a proglacial lake, formed in the Lake Superior basin more than 10,000 years ago and served as a precursor to the formation of what is now known as the largest lake in North America.
Characteristics of Lake Superior
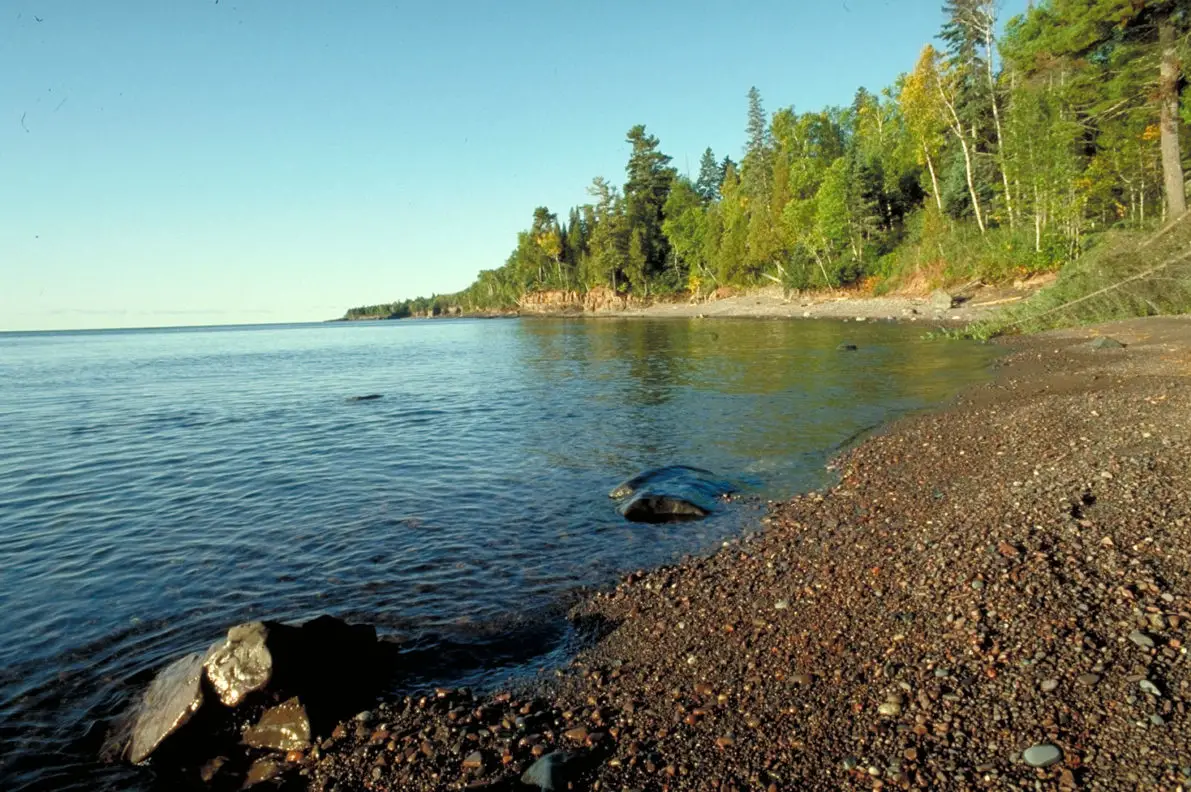
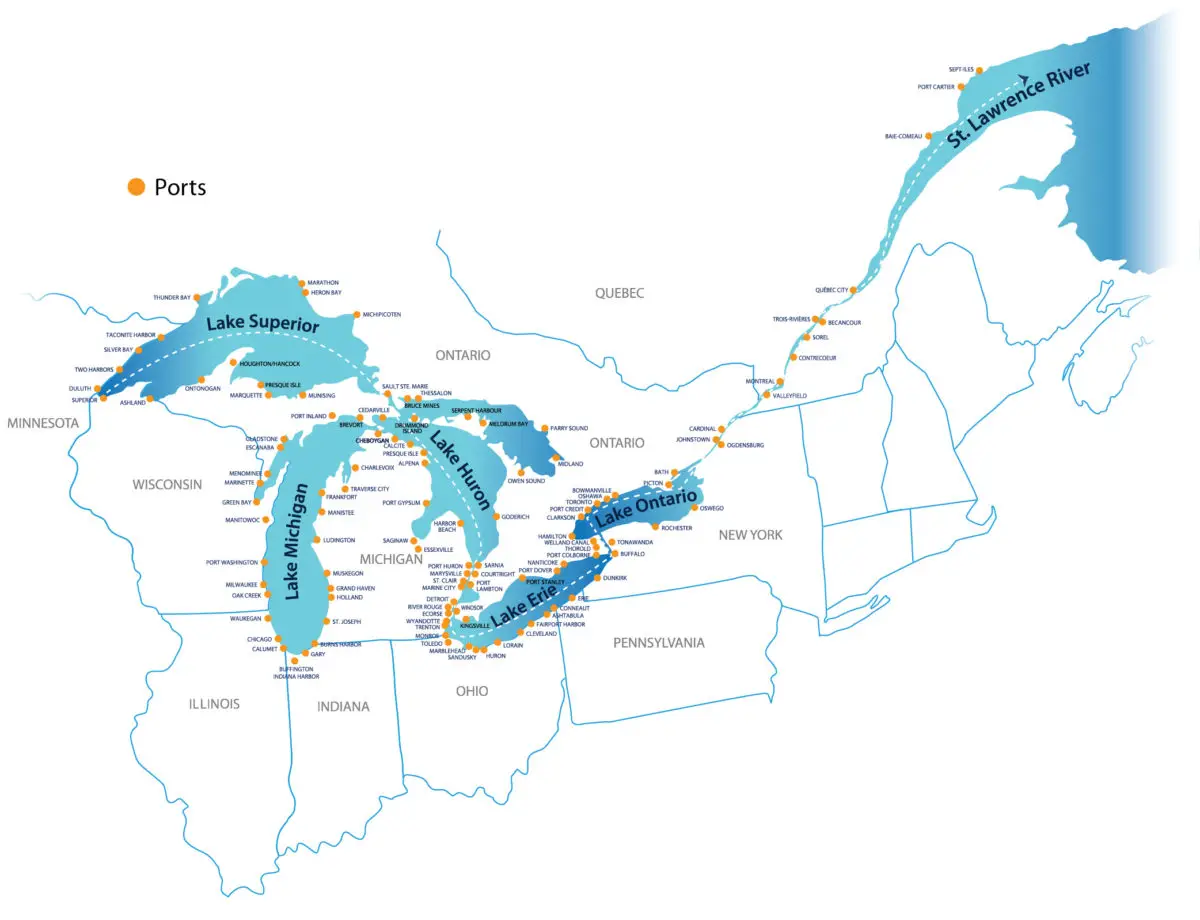
Lake Superior has a number of features that make it one of the largest lakes in North America and the largest freshwater lake in the world, with an area of 82,414 square kilometres, a maximum depth of 406 metres and an elevation of 183 metres. Its watershed reaches the St. Lawrence River and also has a number of tributaries, including Nipigon, St. Louis, Pigeon, Michipicoten and Kaministiquia.
This large lake is 563 kilometres long and 257 kilometres wide. The volume of its waters is 12,232 cubic kilometres and it also has 4,393 kilometres of coastline, including those of its islands, of which there are several.
As already mentioned, this lake is located between the United States and Canada, so its region is bordered to the west by Minnesota, to the northeast by Ontario, which is part of Canada, and to the south by Michigan and Wisconsin.
Another feature is that it flows into Lake Huron, another large body of water in central North America, via the St Mary’s River, one of its tributaries.
Lake Superior is generally less polluted than the other Great Lakes, thanks to a 1972 pact between the two nations that own the lake to prevent pollution.
The lake is fed by more than 210 rivers and is the largest, deepest and coldest of the lakes in the group. During storms, the lake has record breaking waves of more than six metres, and there have even been reports of nine metres.
A remarkable aspect of this lake is that in 1985 a scientific expedition reached 223 metres below sea level, which is considered to be the lowest point in the interior or continental United States, when limnologist J. Val Klump reached the deepest part of Lake Superior for the first time.
Climate of the Lake
The climate of the upper lake is temperate, with mild winters and cool summers, with an average annual temperature of about 7°C, but with variations when the wind blows, which is particularly noticeable on its shores and on all the surrounding slopes.
Fog is noticeable in late spring and generally in autumn. This phenomenon, when it occurs during the warm season, is due to condensation in the air from the water running off this cold lake.
In regions such as Duluth, fog lasts an average of 52 days a year and is a major tourist attraction in the area. It should be noted, however, that the increase in snowfall does not have a pronounced effect on the climate. However, in areas such as Michigan, snowfall can be as high as 350 inches.
But in the Duluth area, where the air itself cools all the moisture, the average snowfall is only 55 inches. In general, the lake can freeze completely during snowfall, trapping heat and preventing evaporation, but this natural phenomenon has changed over the past 30 years, with a significant decrease in ice cover.
Flora, Fauna and geology
The vegetation of Lake Superior is represented by oak forests found on the shores of the lake, along with other hardwood species, as well as pine forests. In general, there are also a number of mosses, ferns, reeds, rushes and algae in all the underwater areas of the lake.
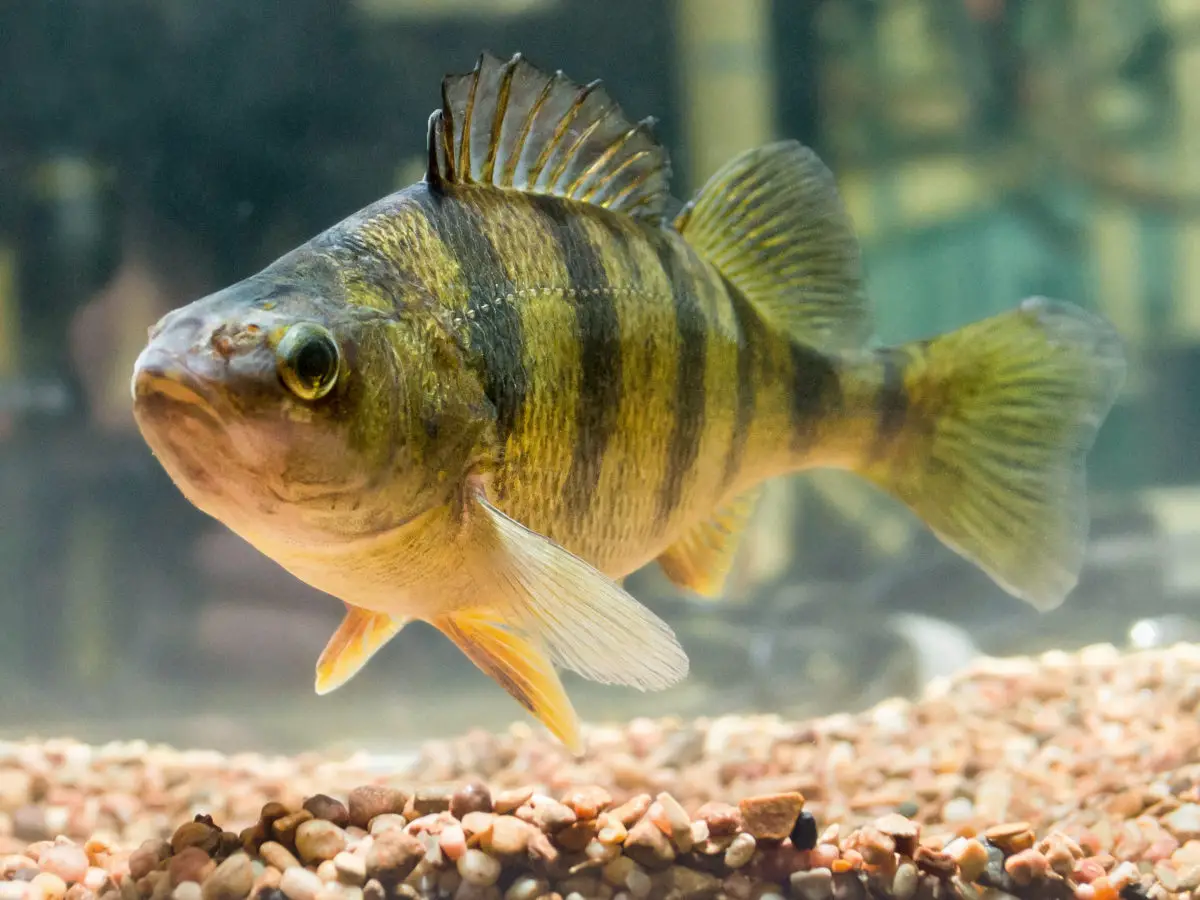
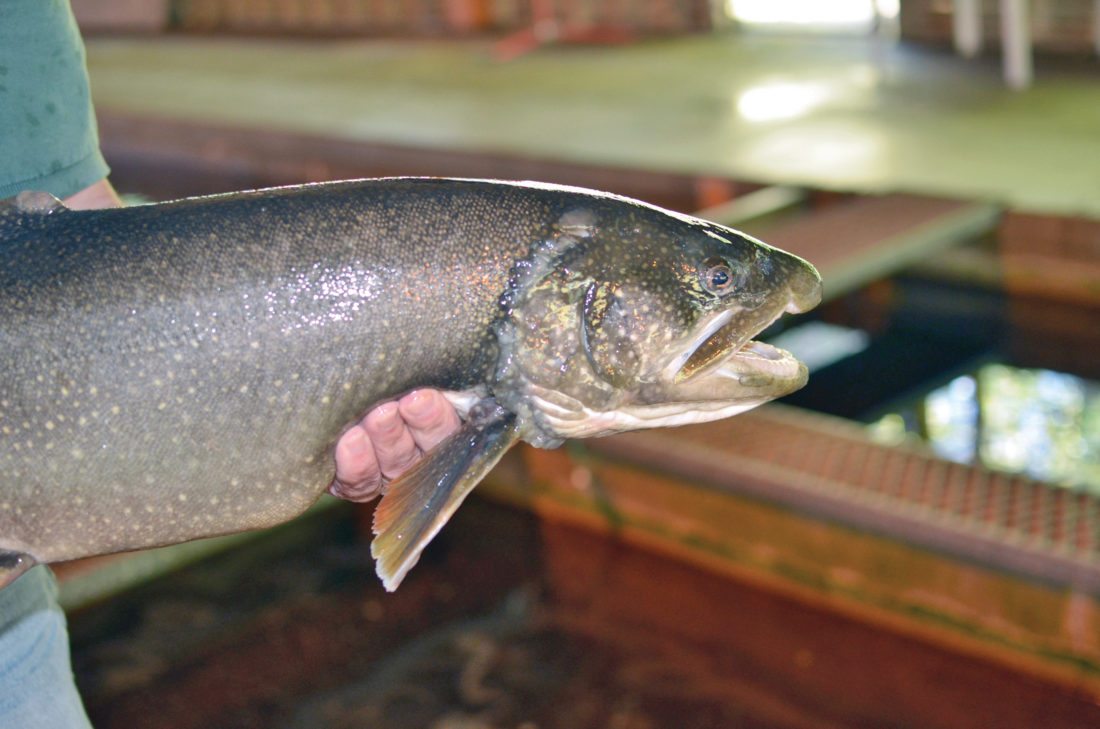
As for the fauna of the place, it is said that there are more than eighty species of fish, most of them autochthonous, among which we can mention: trout, wirefish, white fish, longnose sucker, white matalote, smallmouth bass, cisco, burbot, lake sturgeon, yellow perch, and many others.
Some species have also been captured for the purpose of cross-breeding in order to obtain greater diversity, such as Atlantic salmon, freshwater drum, trout, carp, sea lamprey, white perch, rainbow smelt, etc.
The yellow perch, one of the species that make up the fauna of Lake Superior, has the peculiarity of being able to live in both fresh and salt water, reaching a length of up to 35 centimetres.
Trout, on the other hand, are related to salmon and are found only in freshwater, although, as mentioned above, they are not native to the area, but have thrived once introduced to these waters.
In summary, Lake Superior is home to more than 850 species of animals and about 500 different species of plants. These include unique species such as the Pusa Caspica, a seal found nowhere else in the world. There is also the sturgeon, abundant in the waters of the lake, whose caviar is very luxurious in the markets.
The fauna, however, varies according to the characteristics of the lake in each of its zones, where animals such as the beaver can be observed, a rodent that likes to build natural dams that in some way help to regulate the depth and extent of the water.
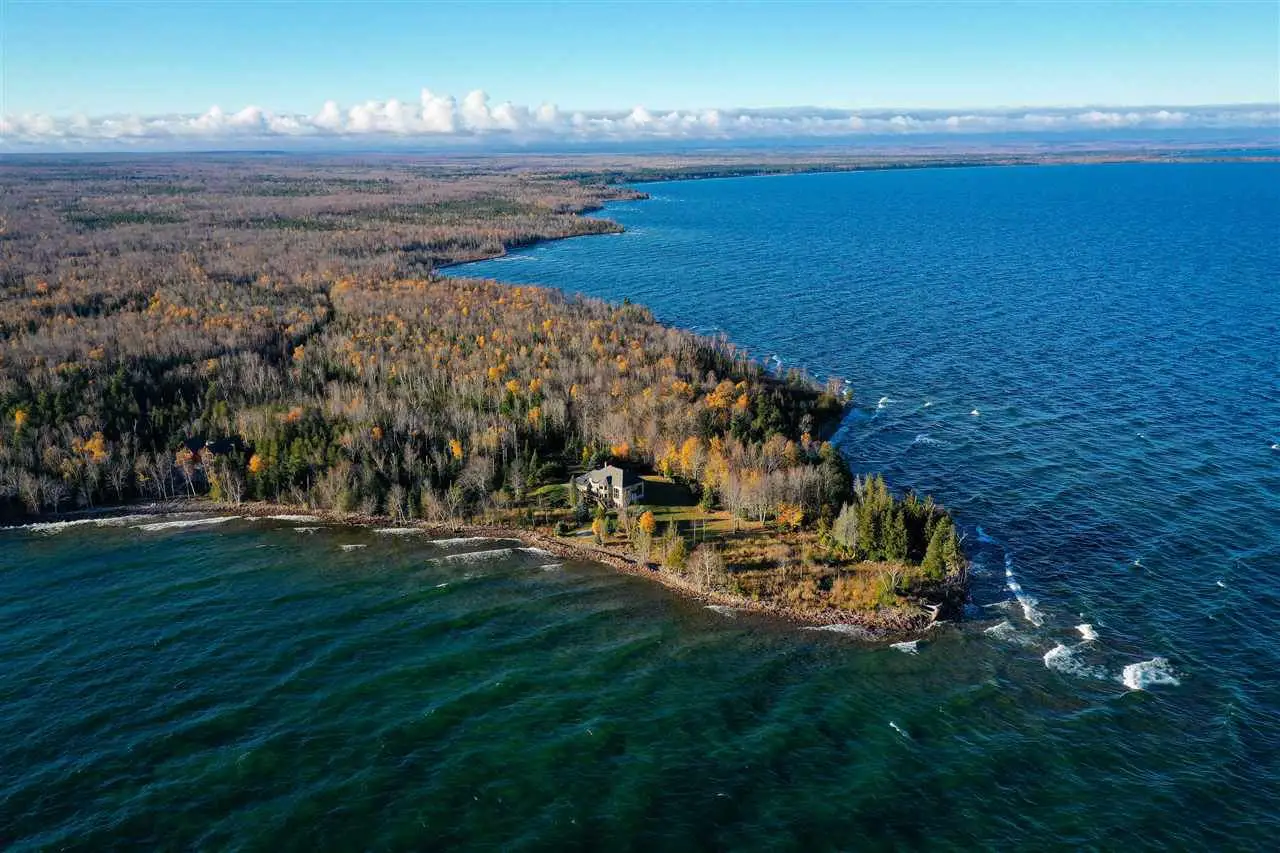
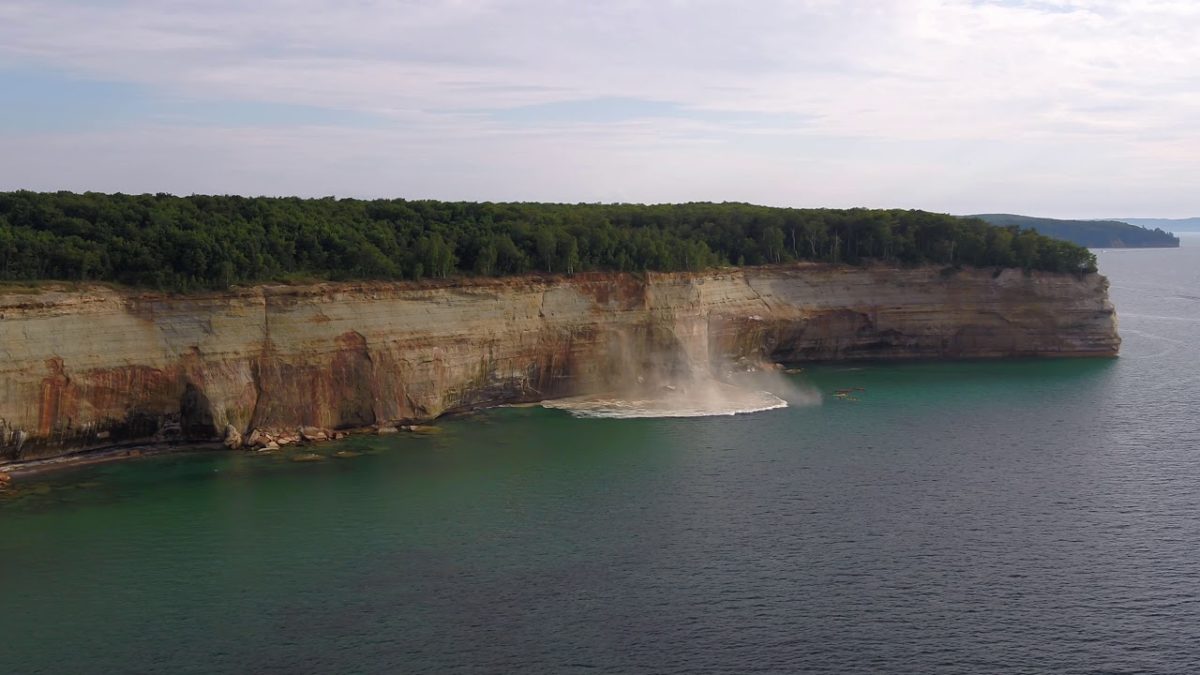
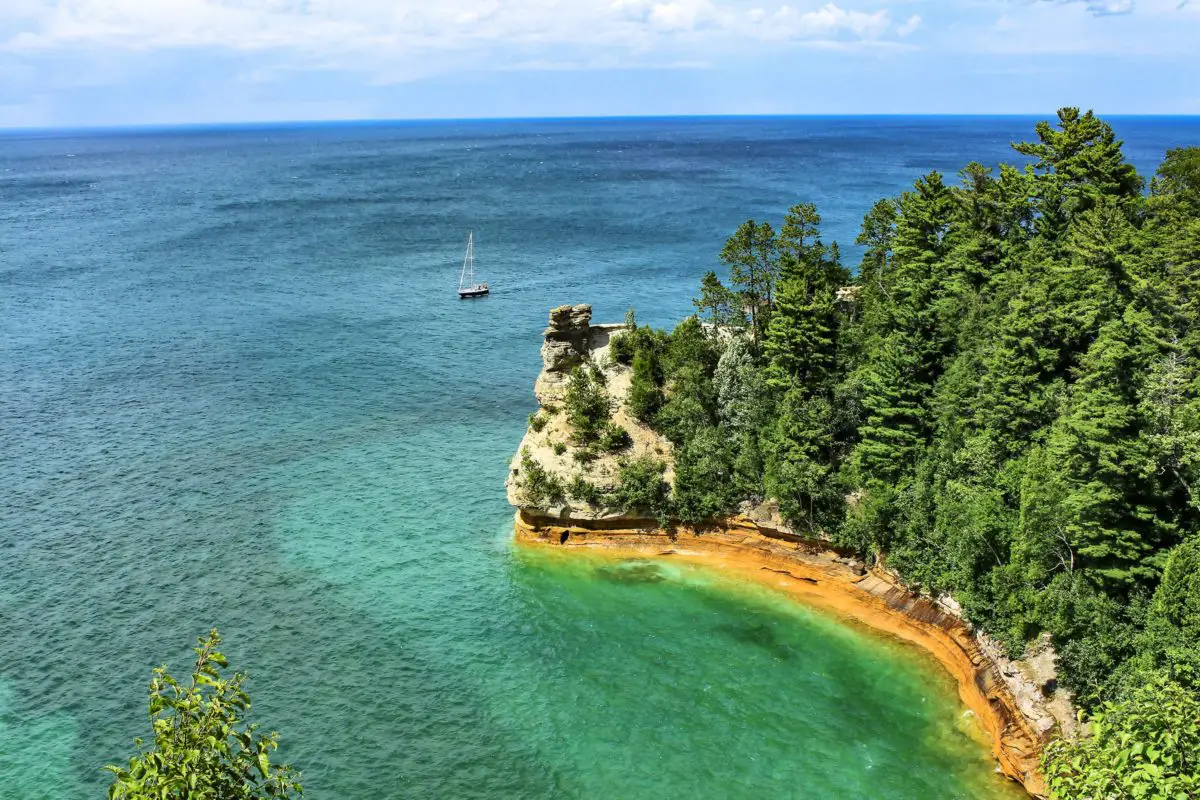
With regard to its geology, as mentioned in the development of the origin of this lake, it is formed by sandstone cliffs, which are also usually unstable and easily detached.
It is a freshwater lake, created because its waters have been isolated due to various reactions or changes in the tectonic plates, as well as the influence of the climate.
However, it should also be noted that many parts of this lake, like other lakes, suffer from deformations, either due to human activity in them, or due to natural influences caused by the impact of the rivers that flow into them, or simply by the movement of the current tectonic layers, which in many cases alter the course of its waters, causing them to be territorially modified in this sense.
It is this factor that causes the lake to have more or less coastal areas in certain places over the years, which can be scarce or very prolonged due to the influence of climatic changes and alterations related to the rainy seasons.
Lake Islands
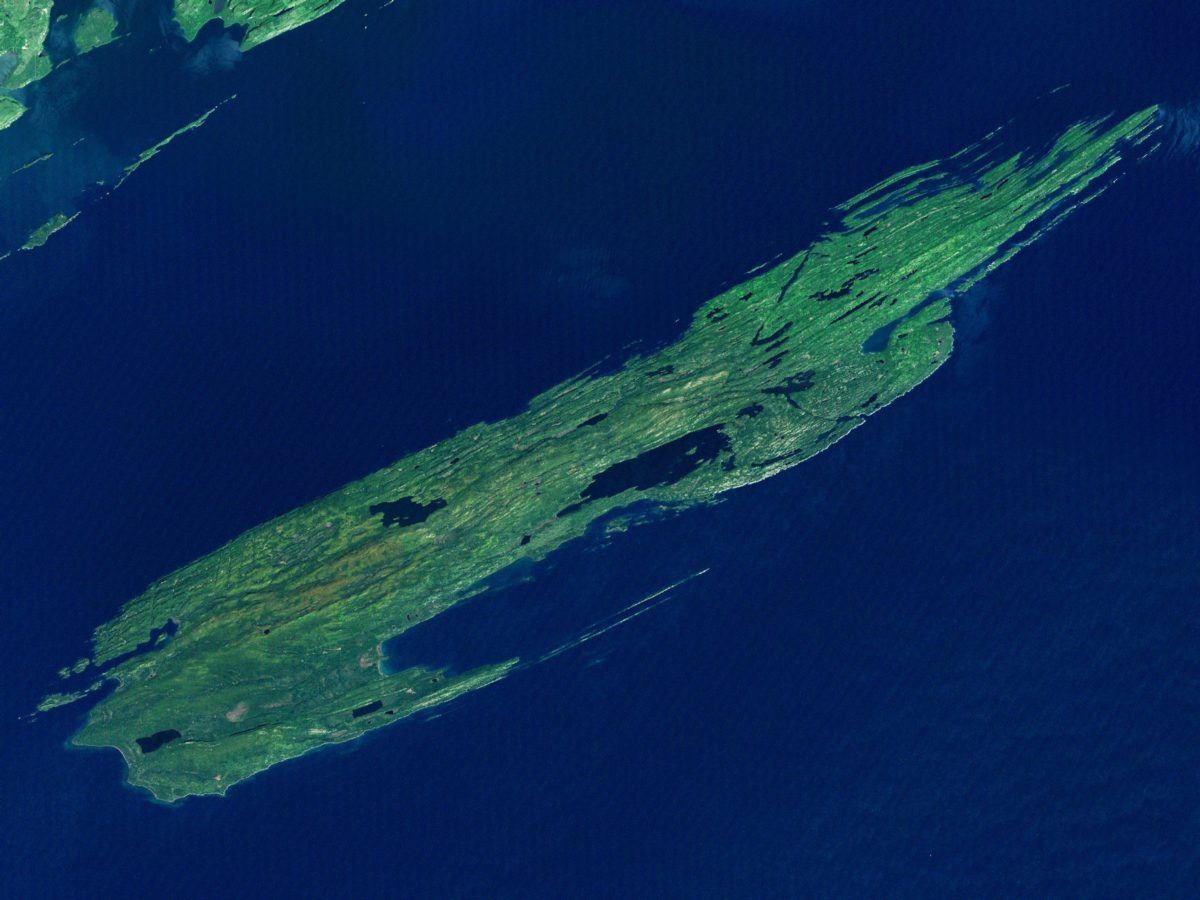
This lake has a number of islands within its vast river area, the largest of which is Royale Island, which belongs to the state of Michigan. Interestingly, this island has several lakes within it and at the same time these lakes have other smaller islands.
Another island that stands out as part of Lake Superior is Madeline, which is in the state of Wisconsin, and the so-called Michipicoten Island in the province of Ontario, which belongs to Canada.
Royale Island
Considered the largest island in a lake, it belongs to the state of Michigan in the USA and has an area of 535 square kilometres; it is 72 kilometres long and 14 kilometres wide.
Located in the northwestern region of Lake Superior, it is surrounded by about 450 small islands that make up the Isle Royale National Park, which, in addition to this chain of islands, has about 4 miles (7.24 km) of shoreline.
It is worth noting that this lake was declared a wilderness area in 1976 and later, in 1981, it was declared a biosphere reserve by UNESCO.
Royale Island was the territory of the Ojibwa people and became part of the United States following a treaty with Great Britain in 1783. Subsequently, the Ojibwa ceded the territory to the United States under the Treaty of La Pointe in 1842.
Apostle Islands
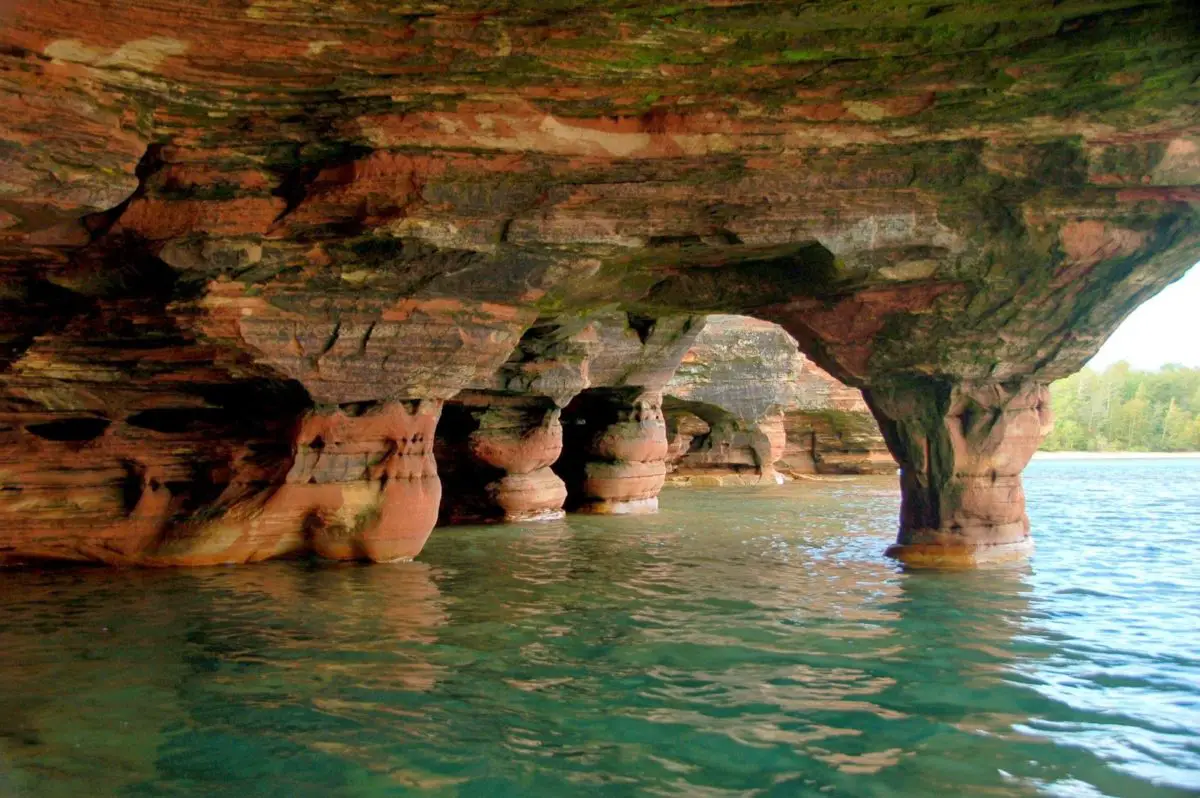
This is another of the impressive places that make up Lake Superior, which has some of the most beautiful underwater caves in the world. These caves are found on the sides of islands, of which there are 22 in total, but twelve of them are large enough to be more significant, hence the name Apostles.
Of these, the smallest, called Gull Island, is one hectare in size. Most of these islands have caves and tunnels on their sides, many of which are inaccessible and dangerous, and must be explored by experts in the field.
These caves are a wonderful sight in winter, when visitors can walk into them from the shore when the ice is completely frozen.
Where does Lake Superior flow into the lake?
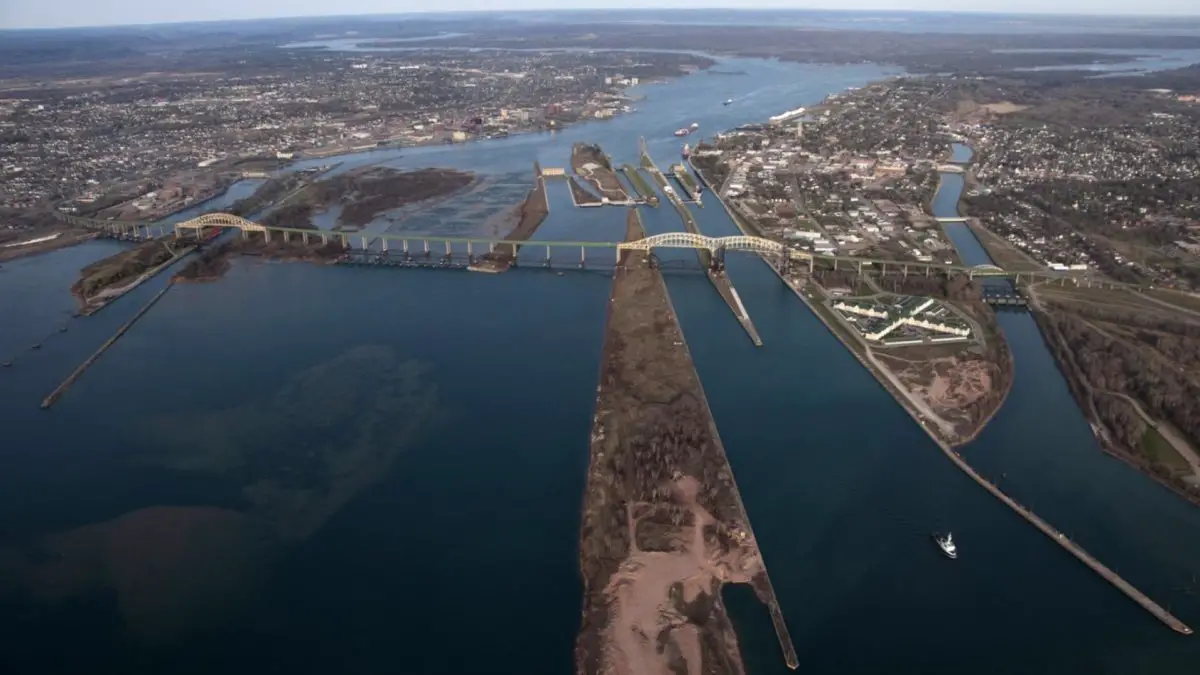
Lake Superior flows into Lake Huron via the St. Marys River, which is part of the Canadian province of Ontario. This lake, known as Lake Huron, is one of the five Great Lakes of North America, the other four being Michigan, Erie, Ontario and Superior, of which Superior is the largest and longest, followed by Lake Huron. They are all great wonders of nature tourism.
By estimating the water content of Lake Superior, it has been found that it can fill the other four lakes and would still have water available to replenish some other basins.
As mentioned above, Lake Superior is drained by the passage of its waters into the St. Marys River, a short tributary of the Ontario region that begins at the tip of Whitefish Bay and flows southeast for 120 kilometres to enter Lake Huron, where it carries the waters of Lake Superior.
The river is part of Canada’s national heritage and forms an international border with the state of Michigan in the United States. It is also part of a river system represented by the St. Lawrence River, which belongs to the United States and is a collector of the Great Lakes, connecting to the Atlantic Ocean.
Outstanding localities
Being such a large lake, it has enough territory for the establishment of large cities along its course, as there are several islands and surrounding areas where these urban settlements have been developed.
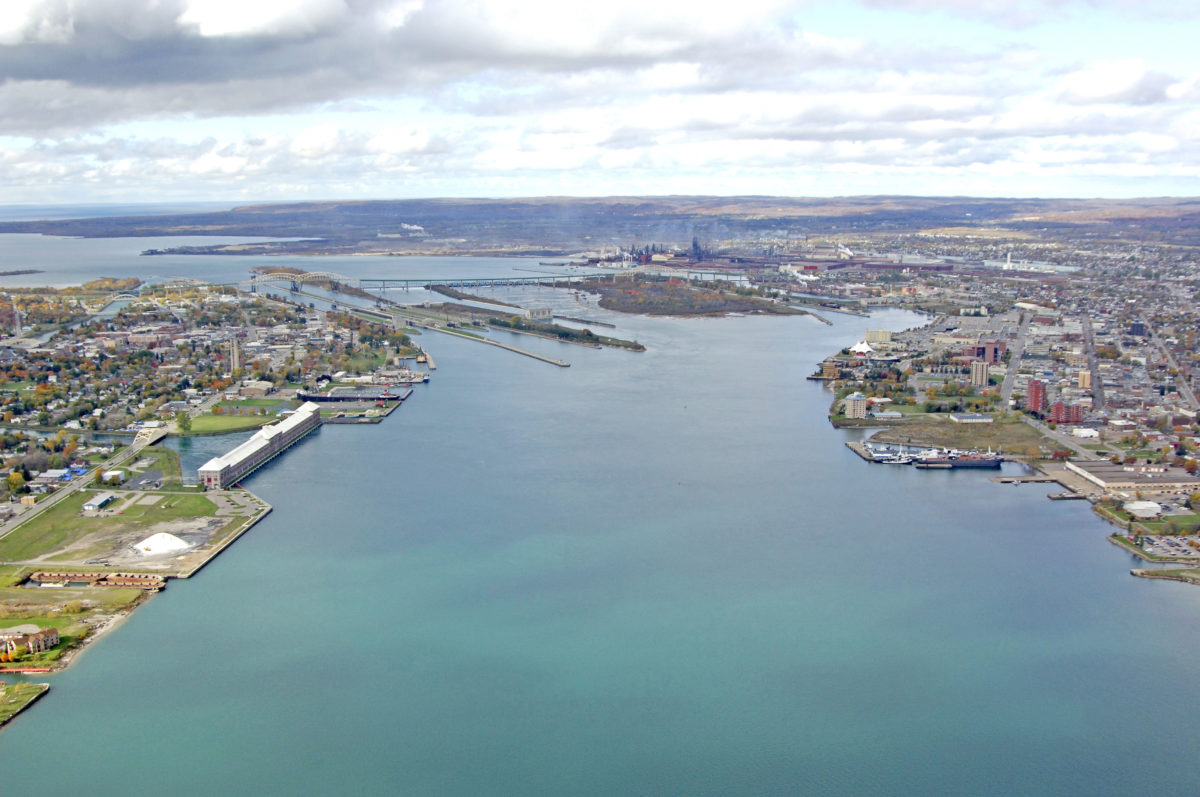
Some of the cities are of great importance, mentioning in this sense the twin cities of Duluth and Superior, located in cities with ports connected to the Atlantic Ocean, belonging to Minnesota and Wisconsin.
Also the twin city of Sault Ste. Marie, belonging to Michigan, with Sault Ste. Marie of Ontario, Canada. On the other hand, there is Thunder Bay to the north-west of Lake Superior, which belongs to Canada, and Marquette to the south of the lake, which corresponds to Michigan in the United States.
It is worth noting that some of the towns around Lake Superior are involved in mining or make their living from this type of work.
It is also an attractive site for adventure tourism because of its rugged shoreline and many deserts. The lake is also used for metal transportation as it supports the heavy traffic of boats that normally travel to Lake Erie, which forms part of the Great Lakes between the United States and Canada.
Temperature problems in Lake Superior
Lake Superior is showing signs of problems that may be linked to climate change, as evidenced by scientific studies based on the fact that it is at its lowest level in decades.
It is unbelievable that this lake should give an image of vulnerability when it is deep enough and covers such a large area that it has been compared to the size of South Carolina, but the fact is that its water level has been falling.
Studies have shown that the average water temperature has risen by two degrees since 1979, as has the air temperature in the region, which is strange for a lake that originated from a melting glacier, from which it gets its fresh water, and which has generally remained cold in all seasons.
Incidentally, a meteorological instrument has been installed on the western side of the lake to measure the weather in the region and has provided some surprising information, registering 24 degrees Celsius, a temperature never before recorded in these waters.
Professor Jay Austin, a member of a group of scientists from the University of Minnesota who have been monitoring the temperature problems of Lake Superior, points out that this figure is unusual for the characteristics that the lake has been experiencing over the years, where the water level is also falling.
This is something that many of the other lakes in the region have been experiencing since the late 1990s, according to the work of the Great Lakes Observatory in Duluth. But the situation in Lake Superior is alarming because the changes it is experiencing are sudden and considered serious.
This is causing anxiety among many of the people living in the surrounding areas, who can see that the shorelines have risen by tens of metres and are now much wider than they were in the past, giving bathers more beaches, but also more shorelines revealing the presence of filth and vegetation in a state of decay, which is a cause for concern.
Without the need for professional instruments and by observation alone, residents of the Sault Ste. Marie area, such as Dan Arsenault, have commented that after thirty-two years of living in this region and watching his children play on the beaches of Lake Superior, the water that used to be waist deep for his children is now just mud.
Similarly, a floating buoy that used to mark the limit for swimming is now completely submerged, and everyone claims that the lake is at the lowest level they have ever seen it.
There are also some problems with the use of the jetties, where boats find it very difficult to dock, even though there is plenty of water and the average depth has been set at 147 metres. Boats are also having problems using the docks and the government needs to step in and dredge all the shallow bays.
But it is not just people who are affected: the fauna of Lake Superior, especially the fish, are also affected by the warming waters, especially species such as the perch, which have been attractive to many sport fishermen, and which are migrating to colder waters.
This causes a number of inconveniences for the shipping industry operating on Lake Superior, resulting in millions of dollars in losses. Ships carrying mineral cargoes carry less weight to avoid running aground in shallow water, delaying trade.
What to see on Lake Superior
Lake Superior has a number of places that are ideal for tourists and adventurers who want to get in touch with nature. There are recreational areas such as the Apostle Islands National Lakeshore Park, which has a number of rock formations, beautiful beaches and caves that are part of its natural heritage.
Up to 800 plant species can be found here, as well as a variety of land animals such as deer and rabbits, as well as birds and a variety of fish, which are very attractive to those who enjoy sport fishing.
It has, among other things, with walks towards its islands, allowing the realisation of activities such as kayaking or simply collective tours in boats, with many places to camp and, of course, to practice hiking.
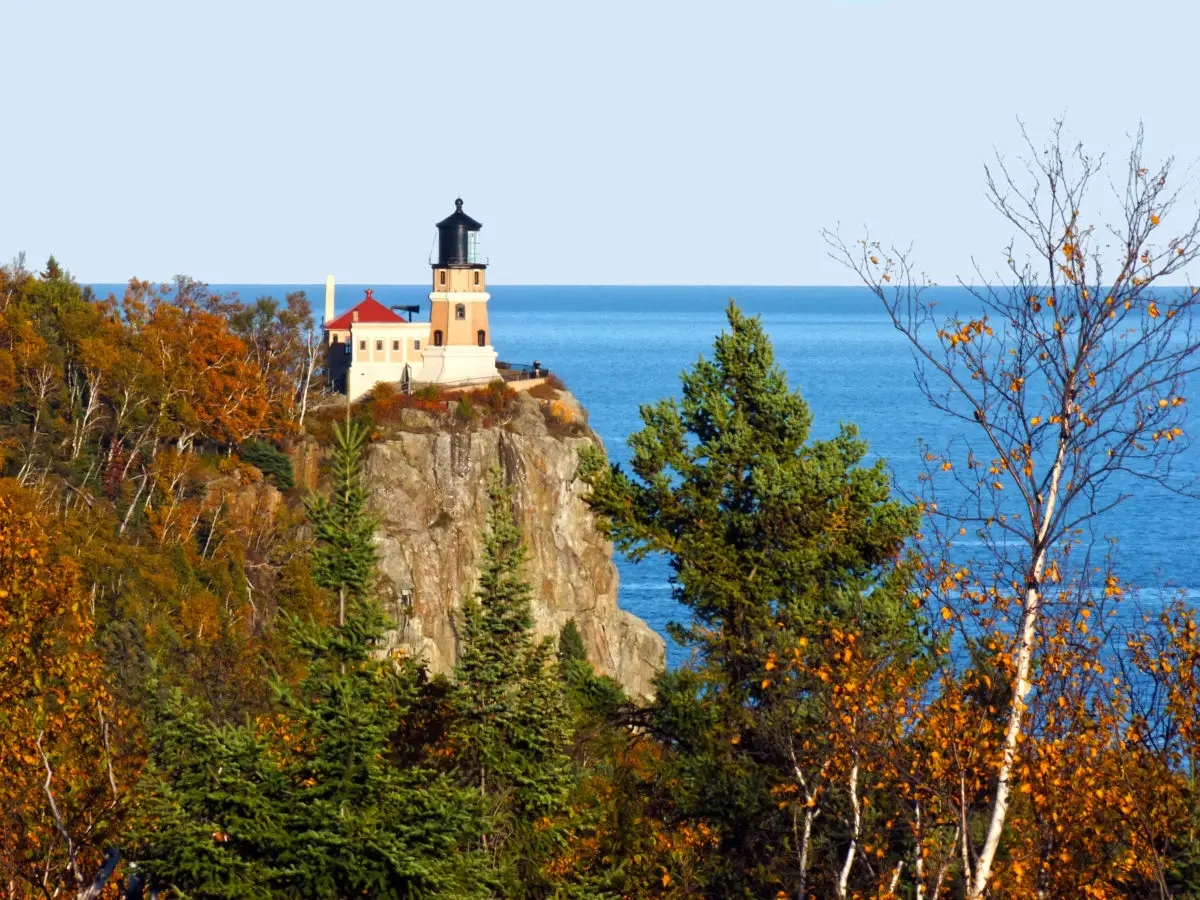
On the other hand, you can visit many of its beautiful and interesting cities, such as Duluth, in the north of the state of Minnesota, which corresponds to one of the edges of the lake. You can also visit scenic areas such as Isle Royale National Park, Porcupine Mountains Wilderness State Park, Lake Superior Provincial Park, Ontario’s Sleeping Giant and Pukaskwa National Park.
In addition, many professional photographers come to Lake Superior to take beautiful postcards of the rock formations that line the shores of this great lake.
Importance of this Great Lake
Lake Superior is famous for its many islands, the largest of which is Royale Island on the Michigan side of the lake, but it also has its own inland lakes with a number of small islands or islets.
Lake Superior is home to several major cities, as well as some of the surrounding natural parks. There is also the Great Lakes Circle Tour, a large system of highways used for automobile traffic that also offers impressive panoramic views as it crosses the five great lakes and even the St. Lawrence River.
On the other hand, and also of great importance, is the fact that in 1921 a number of canals with locks and gates were installed on the Saint Mary’s River, with the purpose of facilitating and allowing boats to navigate its waters without having to face the rapids.
The Saint Mary’s River runs through the city between Lake Superior and Lake Huron, just south of the U.S. Locks, and the Edison Sault Electric hydroelectric generating station is the longest in the world at 408.4 metres. It generates up to 30 MW of electricity, which is very important for the whole region.
As far as boat traffic on the river and lake is concerned, services are closed during the winter season, from mid-January to the end of March. But with the arrival of summer, more than three million tourists visit this area, which is presented by Lake Superior, to visit, walk or simply camp in the wilderness surrounding this lake.
This is a good time to invite all our readers to get to know Lake Superior, the largest freshwater lake in the world and one of the Great Lakes of North America, which forms the natural border between two important nations: the United States and Canada.
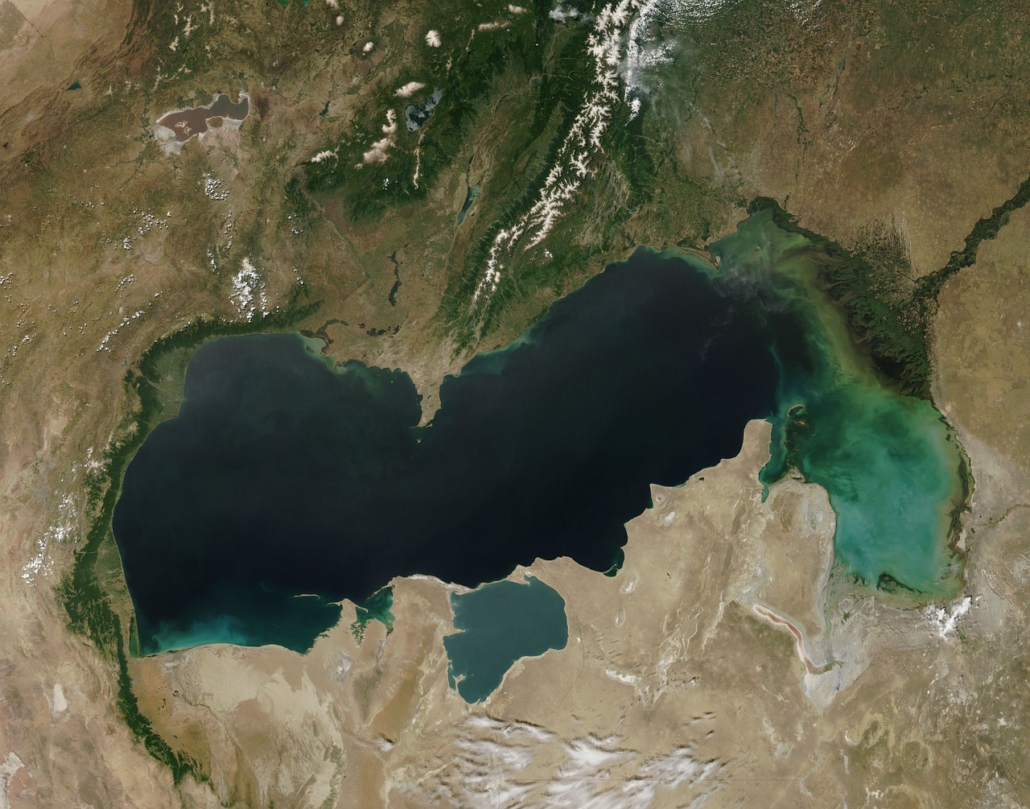
Map of the lake
Below is a map showing the exact location of Lake Superior, which lies between the United States and Canada, crossing the states of Michigan, Minnesota, Wisconsin and Ontario within these countries.
If you have enjoyed the information in this article, we invite you to discover more rivers through the following links:
- River Sella
- River Bidasoa
- River Guadalete
- Magdalena River