The San Francisco River is important to Brazil, also known as the “River of National Integration”, because of its diverse climates and landscapes, especially in the southeast with the northeast.
In 1865, the British explorer and diplomat Richard Francis Burton was transferred to Santos, Brazil. To explore the centre of the mountains, down the San Francisco River from its source to the falls of Paulo Afonso.
Indice De Contenido
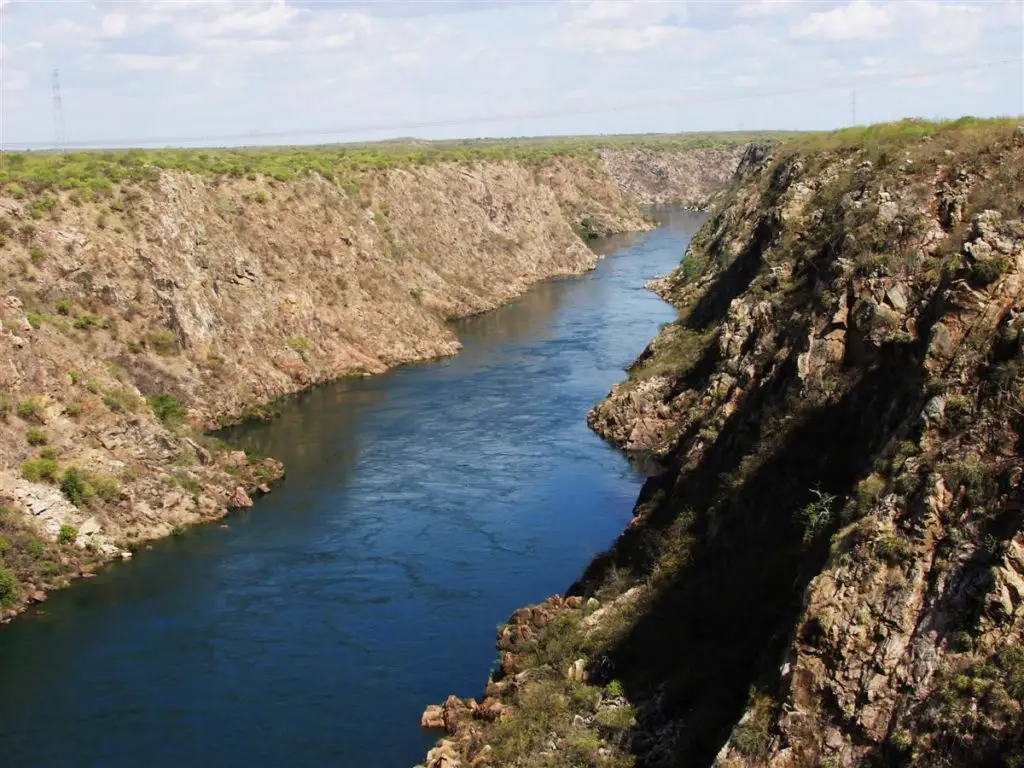
Location of the São Francisco River
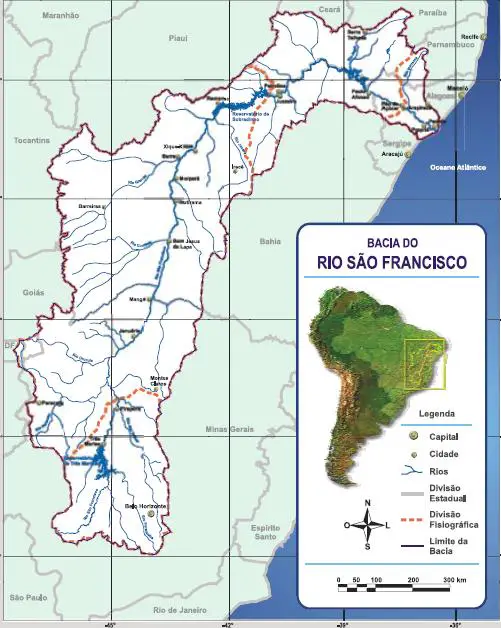
The São Francisco River rises in the Canastra mountain range in the central-western part of the state of Minas Gerais. It generally flows northwards to the states of Minas Gerais and Bahia, behind the coast.
It drains an area of over 630,000 square kilometres (240,000 square miles) before turning east to form the border between Bahia on the right bank and the states of Pernambuco and Alagoas on the left (see article: Paraná River).
It then forms the border between the states of Alagoas and Sergipe and flows into the Atlantic Ocean, as shown on the map of the San Francisco River in Brazil. In addition to the five states that the São Francisco flows through or borders, its drainage basin also includes tributaries of the state of Goiás and the Federal District.
San Francisco River Argentina
It rises near San Pedro at the confluence of the Lavayén and Grande Rivers. It flows in a north-easterly direction in a tropical rainforest environment. Shortly after entering the province of Salta, it joins the Bermejo River near the town of Pichanal (see article on the Segura River).
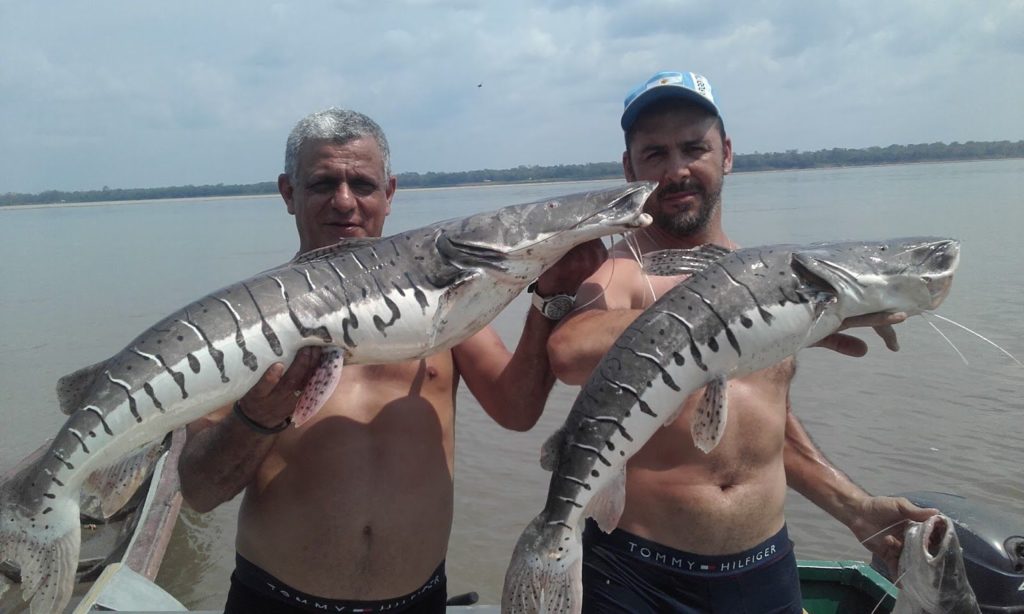
Fish species in the San Francisco River
More than 200 species of fish are known to occur in the San Francisco river basin and it is expected that many more will be discovered in the future, especially in the relatively unknown upper reaches of the river.
About 10% of the known fish species in the basin are threatened and about 13% are important for fisheries. About 64% of the known fish species in the basin are endemic.
These include Conorhynchos conirostris (a catfish of uncertain taxonomic affinity), Lophiosilurus alexandri (a flattened catfish), Franciscodoras marmoratus (an armoured catfish), Pygocentrus piraya (the largest species of piranha), Orthospinus franciscensis (a characin and the only member of its genus) and Salminus franciscanus (a relative of the golden bream).
More than 40 species of annual killifish are found in the San Francisco River basin, mainly in the genera Cynolebias and Simpsonichthys. Dams (which prevent fish migrating up the river) and pollution are a problem for the species in the river, and massive fish kills have been recorded (see article: Rio Balsas).
The San Francisco River is naturally navigable all year round between Pirapora (Minas Gerais) and the twin cities of Petrolina (Pernambuco) and Juazeiro (Bahia), with a length of 1,371 kilometres (852 miles).
However, there are large variations in depth depending on rainfall. Due to the variety of physical characteristics along the navigable section, it can be divided into three sub-sections, as follows
- From Pirapora to Pilao Arcado (Bay), a length of 1,015 kilometres (631 miles); differences in elevation of up to 6 metres (20 feet) can occur due to rainfall and drought.
- From Pilao Arcado to the Sobradinho dam; the reservoir of the latter is 314 kilometres (195 miles) long, with a surface area of 4,214 square kilometres (1,627 square miles) and a comfortable depth.
- From Sobradinho dam to Petrolina – Juazeiro, with a length of 42 kilometres (26 mi) and an average depth of 2 metres (6 ft 7 in), maintained by a flow of 1,500 m3/s (53,000 cu.ft/s).
Tourism
Until recent years, the San Francisco River was regularly navigated by a type of passenger boat called a gaiola (Portuguese for “cage”). These were paddlewheel steamboats, some of which were Mississippi River riverboats, dating from the American Civil War era.
After the construction of the Sobradinho dam in Bahia, the navigability of the lake changed considerably, as the large size of the reservoir allowed the formation of short waves of considerable height.
Although the dam did not block navigation, the waves and currents made it difficult for the gaiolas to cross the lake. At the same time, deforestation and excessive agricultural use of the waters of the upper reaches of the San Francisco and its tributaries greatly reduced the flow of water in the middle reaches, creating sandbars and islands that hindered navigation.
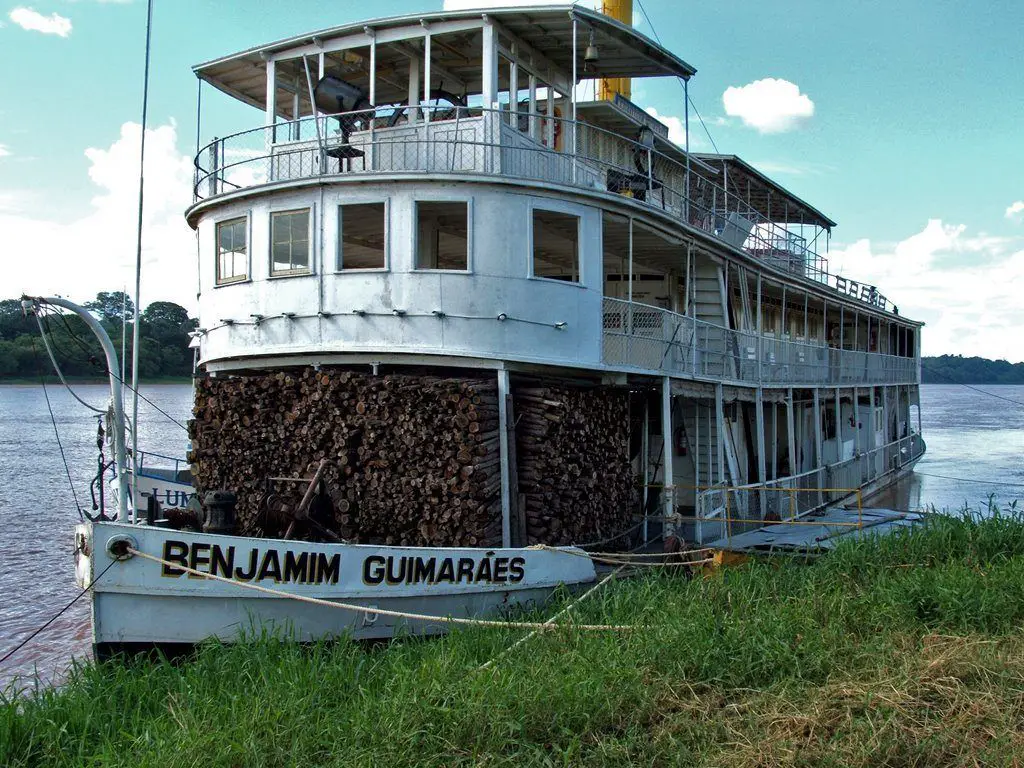
Soon conditions were such that navigation became impossible for large gaiolas, although it was still possible for smaller vessels. The hulls of these old boats can still be seen in the river at Pirapora.
As of 2009, only one boat remains in operation, the Benjamim Guimaraes, which makes short tourist trips from Pirapora to San Roman and vice versa.
Here is a video about navigation on the San Francisco River.