Last Updated on September 11, 2023 by Hernan Gimenez
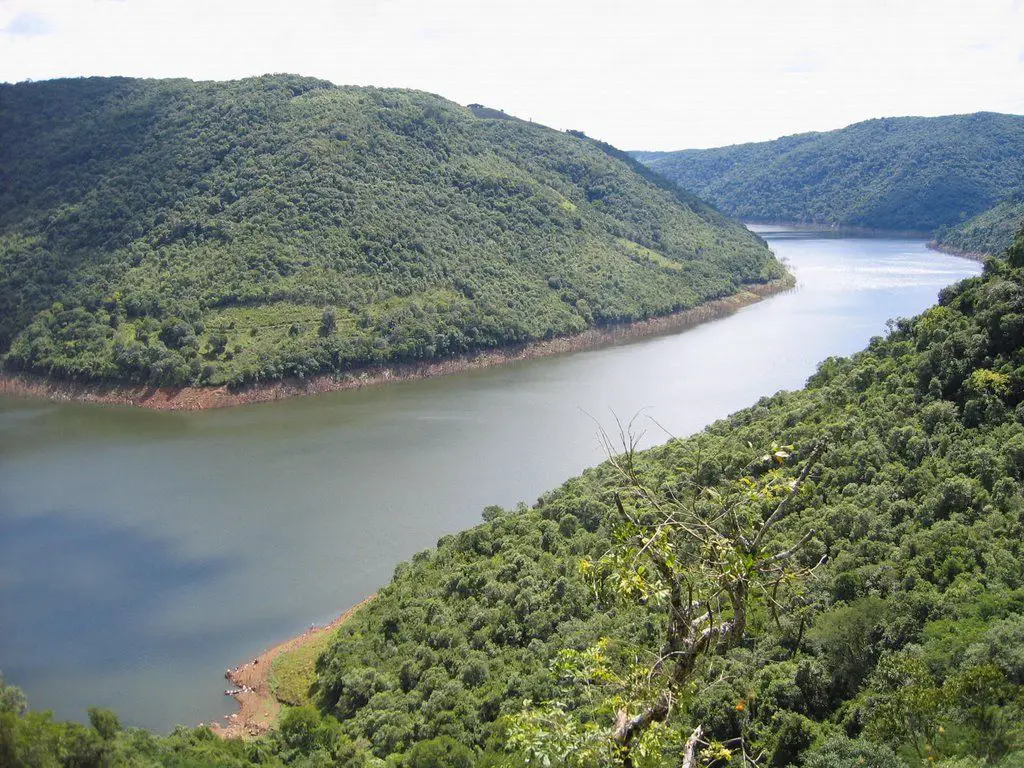
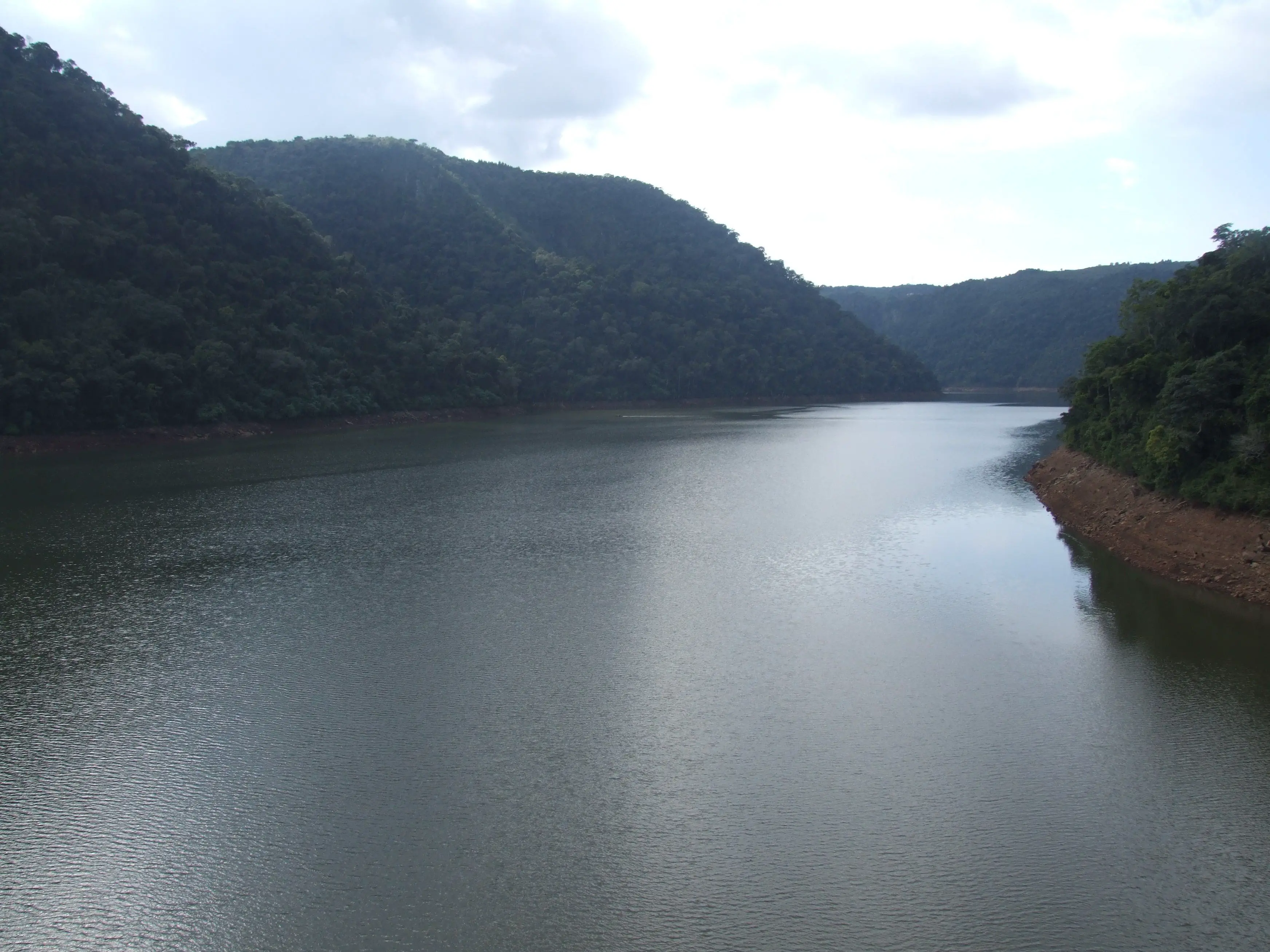
The Uruguay River is a shared river between Brazil, Argentina and Uruguay. The Uruguay River also has a length of 1,800 km, which together with other areas forms the Silver Account, find out all about it here!
Known in Portuguese as the Uruguai River, it was discovered on 10 and 13 January 1520 by an expedition from the ship Santiago, led by Captain Juan Rodríguez Serrano on a voyage to discover the world.
At the beginning, the river was called “San Cristobal River”. Over the years, the name was changed several times, until it was finally given the name of Uruguay River, which is logically where the river ends. Since it is shared by Brazil, Argentina and Uruguay, it is divided into two parts: the Upper Uruguay River and the Lower Uruguay River.
Indice De Contenido
Characteristics and Location
Among the characteristics of the River Uruguay, it presents all kinds of denominations, being an important river, when talking about characteristics, they are divided into: upper, middle and lower.
- The upper parts of the Uruguay River are not so navigable because its flow is very fast. It is 816 km long and has a gradient of 43 cm/km from the confluence of the Pelotas and Canoas Rivers to the Piratiní River.
- The middle section of the river is shorter, 606 km long, with a gradient of 9 cm/km. It is located between the mouth of the Piratiní River and the Salto Chico waterfall, south of the Salto Grande dam.
- The lower part has the lowest gradient of all, 3 cm/km. It is presented by Salto Chico and Punta Gorda, making it the shortest of all at 348 km.
After the confluence of the Cuareim River, the environment is made up of many islands and many rocky bottoms and basalt outcrops.
It has operations in Brazil, Argentina and Uruguay. Its divisions are as follows:
- Santa Catarina, en Brasil.
- Río Grande del Sur, en Brasil.
- Misiones, en Argentina.
- Corrientes, en Argentina.
- Entre Ríos, en Argentina.
- Artigas, en Uruguay.
- Salto, en Uruguay.
- Paysandú, en Uruguay.
- Río Negro, en Uruguay.
- Soriano, en Uruguay.
- Colonia, en Uruguay.
Height and length of the Uruguay River
Because it is divided between the important countries of Brazil, Argentina and Uruguay, in that order, it has different dimensions, due to the different climatic and environmental conditions of the three nations.
The height of the Uruguay River is 440 metres at its source, 1800 metres at its upper reaches and 0 metres at its mouth.
As for the length of the Uruguay River, we have a length of 1779 km and in Uruguay-Canoas of 2340 km. On the other hand, the width of the Uruguay River from Concepción del Uruguay to Fábrica Colón is 4 kilometres north of the “General Artigas” bridge, and the depth of the Uruguay River is approximately 3.35 metres = 11 feet.
The source and course of the Uruguay River
The source or birthplace of the Uruguay River is the Sierra Geral in southeastern Brazil, near the states of Santa Catarina and Rio Grande do Sul, and the mouth of the Uruguay River is the Rio de la Plata in Punta Gorda, between the department of Colonia and the Argentine department of Islas del Ibicuy, in the province of Entre Rios. It is a very important and long river, like the Rio Bravo.
With a length of 1,838 kilometres and 23 direct tributaries, it joins the Cuareim River in Quaraí, on the border with Brazil, to the north, from where it drops to 35 metres in altitude.
After receiving the Cuareim River, a small tributary that serves as a border between Brazil and Uruguay, forming a triple border between the provinces of Bella Unión, in Uruguay, Monte Caseros, in Argentina, and Barra do Quaraí, in Brazil, its course continues south.
On this southern route, the mouth of the Uruguay River would be further downstream, near the Rio de la Plata.
Tributaries that make up the river
As mentioned above where the Uruguay River begins, which is in the Sierra Geral in southeastern Brazil, and also the mouth of the Uruguay River is in the Rio de la Plata in the Argentine department, we also have that like any river, this has a number of tributaries that integrate and distribute it between the three countries that comprise it are the following:
Brazilian Territory
The Canoas and Pelotas rivers, which flow into the Uruguay River, in Peixe, in Chapecó (248 km), in Pepirí Guazú, on the border with Argentina, Passo Fundo with 200 km, in Várzea, Ijuí, Piratiní with 120 km, Icamaqua and finally Ibicuí with 290 km.
Argentine Territory
There is the Aguapey River with 310 km, the Miriñay River with 212 km, the Mocoretá River with 140 km and then the Gualeguaychú River with 268 km.
Uruguayan Territory
The Cuareim tributary is 351 km long, the Arapey tributary, on the border with Brazil, is 240 km long, the Daymán is about 210 km long, the Queguay tributary is 280 km long, the Negro tributary is 750 km long and, last but not least, the San Salvador tributary is just over 100 km long.
Islands of the Uruguay river
There are many river islands that are considered part of the Uruguay River Treaty of 1961, these are scattered between the border of Uruguay and Argentina. One of the largest is called Cambacuá Island with about 35.67 km2, it is located in the department of Uruguay in Entre Rios, in Argentina.
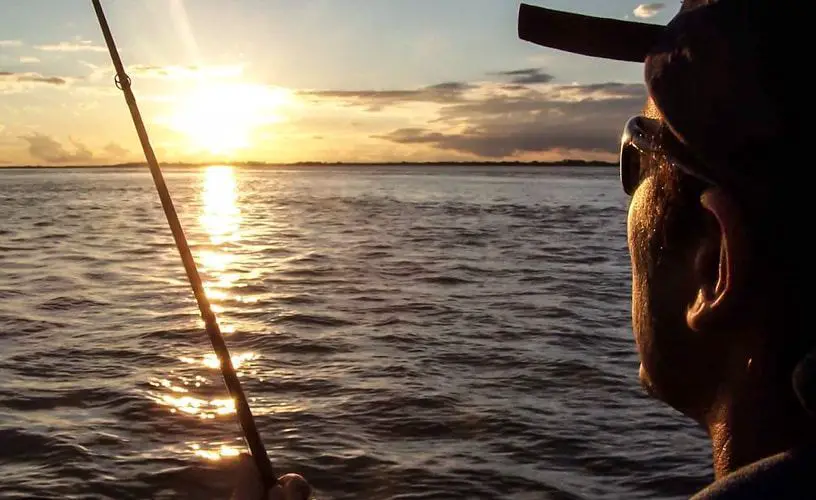
Fishing in the Uruguay River
Thanks to the fact that the Uruguay River is very clear and clean (very similar to the Solimoes River), compared to other rivers in the world and to the Paraná River, which is very close to it, this makes it easier for people to fish. The river has a bed of precious stones, very white and clear sands, at the bottom and along the banks.
It also has colourful rocks that decorate almost all the surroundings. A perfect place for relaxation and sightseeing in many cases. People like to walk along these shores. It is pollution free and the bottom is perfect for artificial lures.
It has very good visibility and a current that makes it an ideal place to catch fish such as bogas and large goldfish. These fish are unique in the world and thanks to the river conditions they grow very, very well.
Thanks to the good ecosystem conditions, the fish have a greenish colour with blue backs that completely cover their bodies and scales. Many people from all over the world come to fish in this river.
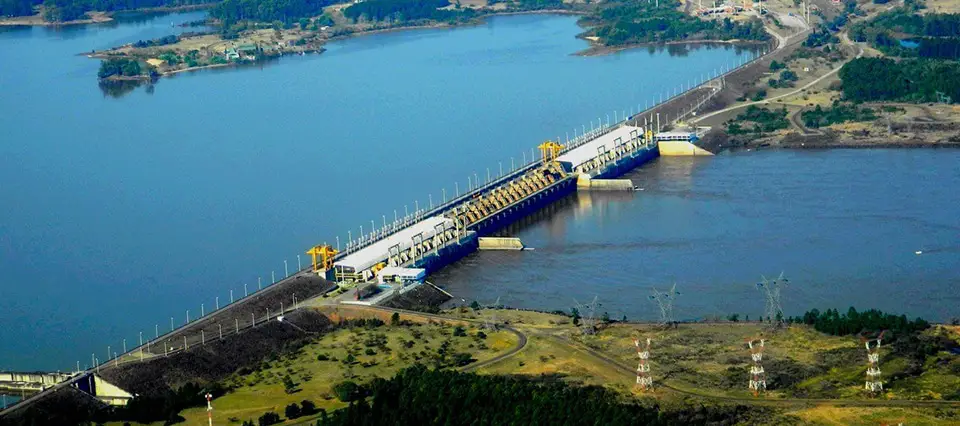
One of the provinces of Entre Rios, Concordia as it is called, is the best place you will find for fishing in this area. One of the reasons is that these waters have the Salto Grande dam. This dam has the function of regulating the water so that it is cleaner and purer, this to achieve a good hydroelectric energy throughout the length of the river in the part of Uruguay.
But when the turbines are turned off, the water pressure drops significantly, which means that the fish cannot reach the river and the river remains low for a long time until the power is restored.
There are other rivers in Latin America where you can also enjoy fishing, such as the Putumayo and Caqueta rivers.
Sport Fishing
It has also been proven that in this river and because of the Uruguayan culture, sport fishing takes place. The locals organise championships and tournaments to reward those who catch a large number of fish.
Fishing is allowed downstream of the dam and many people gather there every year. It stretches from Santo Chico, where most people gather, as there are more fish in this part of the river.
To catch the biggest bogas, maize grains are tangled in the hooks so that the fish can be caught more quickly. You can fish with simple tools like nylon or with heavier and more professional equipment.
People use materials like
- 0.40 millimetre line.
- Big and small hooks.
- Simple bait.
Much or most of the navigability of the Uruguay River is concentrated in the lower part, near the towns of Concepcion del Uruguay and the headwaters of the Rio de la Plata.
As a result, almost all of its stretches and tributaries (like its neighbour, the Tocantins River) are fully navigable, and people even fish there. Everything flows well until you reach the Salto Chico, which, thanks to its waterfalls, comes into conflict with the shipping lane.
Further downstream, the river meanders and slows down near Paysandú and Fray Bentos, a town with darker waters, very similar to those of Nueva Palmira.
Among its main advantages we have that it has a hydroelectric generator located in the middle of the Salto Grande dam, whose property belongs to Argentina and Uruguay, makes the waters of the river flow better.
Now, when we talk about the waters of Brazil, we are talking about the Itá, Foz de Chapecó and Machadihno dams. There has been talk for years that the Brazilian government has proposals to build more hydroelectric plants, one of which will be called Garabí.
It is to be built 7 kilometres downstream from the towns of Garruchos, and its purpose is to provide a lot of water for the electricity it generates.
In addition, the aim is to make the best use of the wasteland that this river has, with activities such as watering plants and sowing seeds, so that there is a large amount of flora to decorate the shores of the lake.
Bridges and Crossings that make up the Uruguay River.
The following bridges are located in the states of Santa Catarina and Rio Grande Del Sur in Brazil:
- Machadihno Dam.
- Railway bridge in Marcelino Ramos.
- Itá Dam.
- Bridge Route BR 470.
- Bridge Route BR 153.
- Bridge Route 480.
- Bridge downstream inside the dam of Itá.
- Foz Chapecó Dam
- Bridge Route BR 480
- Bridge of Iraí
Shared between Argentina and Brazil
- Ferrovial Agustín P. Justo – Getúlio Vargas Bridge.
- Integration Bridge.
Shared between Argentina and Uruguay (most of the Uruguay river).
- General Artigas Bridge.
- Ferrovial the Salto Grande dam.
- Libertador General San Martín Bridge.
Activity that takes place in its ports.
The Uruguay River offers the following ports, where different activities of loading and unloading of ships are developed, as we will tell you below:
Port of Fray Bentos: With the works that have been carried out, this port now has a greater capacity for ships, since it has been enlarged. It also has a large log storage area of around 3 hectares.
Paysandu: This port is mainly used for private activities and is responsible for the movement, loading and unloading of all types of containers, both refrigerated and dry.
Nueva Palmira: A very well located port that continues to receive large investments. This port in particular handles all types of materials, from timber to food products, among others.
Pollution in the Uruguay River
These waters are ideal for recreation, as we have read, and many people have been accustomed to visiting the river for many years, but in recent years numerous bacteria have been found that can affect the place.
Scientists from the Administrative Commission of the Uruguay River, or CARU for short, have published some alarming figures about a number of bacteria that are affecting these waters, although it is not rubbish (or people’s lack of awareness), but microorganisms that are directly attacking the river.
Thanks to the study carried out by this organisation, they registered more than the permitted limit of certain bacteria, a limit of 24 times more bacteria than normal.
These are:
- Faecal coliforms: better known as heat-resistant coliforms, these are clusters of bacteria that come from faecal material and can be born in any type of environment, such as industrial waters, plant compounds and soils in a state of decomposition.
- Echerichia coli: This bacterium is found in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and warm-blooded animals.
- Enterococci: Although enterococci are bacteria that live in the large or small intestine, they are very dangerous because they live in the female genital tract, causing infections that spread to the urinary tract.
In the city of Federación, Uruguay, faecal coliforms range from 600 to 37,600 per 100 ml of water, with an exact average of 2424 UFC/100 ml, which is totally above the values agreed by a direct zone point. This is 12 times more than permitted.
For Escherichia coli, the values reach 300 and 37,300 in some parts of the water and about 126UFC/100, 16 times more than the limit set by CARU.
Although these are the official figures for some parts of this bacterium, there are no exact figures for other areas that have not been well studied by specialists, so for enterococci there are figures from 200 to 5760, with a geometric measure of 812 CFU per 100ml, around 24 times more than the permitted limit.
The coast of Entre Ríos has suffered the most damage because of its proximity to the coast and because it has 24 times the number of bacteria, while the port of Colón has 12 times the number of bacteria.
As a freshwater river, the Uruguay provides clean drinking water for thousands of people and is used for recreational purposes by many adults and children. This is why pollution has been such a problem for the country.
As a result, Uruguay’s major cities have equipped their clinics and hospitals to help patients suffering from bacterial diseases. Many of these viruses cause diarrhoea and vomiting.
Contaminated Cities
- Concordia: has 100 and 9,000 faecal coliforms in every 100 ml of water it makes up, on the part of Escherichia coli there are 70 and 900 in every 100 ml of water, which gives us a final result of 24 times more than the established limit.
- Federation: 600 to 37,600 faecal coliforms per 100 ml of water, more than twice the permitted limit. As for Escherichia coli, between 300 and 37,300 were found on the beaches. Much higher than the others, this would be 16 times the permitted level.
- Puerto Yeruá: between 600 and 5,4000 faecal coliforms per 100 ml of liquid. This is 10 times more than what is allowed, and with Escherichia coli from 100 to 3,700 per 100 millimetres of water.
- Colon: 600 to 6,400 faecal coliforms per 100 ml of water. This is 8 times the permitted limit. Escherichia coli between 150 and 3,300 per 100 ml, 4 times the limit.
- City of Concepción del Uruguay: faecal coliforms are between 140 and 2300 per 100 ml of water, while Escherichia coli are between 25 and 700 per 100 ml, the first city to have low levels of bacterial contamination for the first time.
- Gualeguaychú: 30 and 760 faecal coliforms per 100 ml of water. The Echiceresca Coli is between 10 and 500, which gives a value of 94, and Enterococci is between 30 and 600, which would be 6 times higher than the limit allowed by the World Health Organisation.
In addition, a report was registered stating that there were several stretches of the Uruguay River with phosphorus levels much higher than permitted. To date, no precautions have been taken to prevent or eliminate phosphorus from the river.
Uruguay River and Argentina
It is called Uruguay because a large part of it lies in this country. In this part of the country, it has a surface area of 370,00 km2 and a flow rate of 4,600 m3/s. Together with the Parana, Paraguay and other rivers, it forms the La Plata basin, a very important basin for the countries of southern Latin America.
These waters originate in Brazil in the Sierra General, where they are well connected to the Canoas and Pelotas rivers. Later it receives the river Pepiri Guazu on the right and then you can see a long border between Brazil and Argentina, because after here begins an outlet with the Rio de la Plata, near Punta Gorda, this route is 1,770 km long. This system is called Pelotas-Uruguay and is about 2,340 km long. The last section includes parts of the Parana River.
Although Brazil is one of the three countries that share the Uruguay River, most of it belongs to Uruguay and Argentina, and this has caused problems between the two countries that are still being resolved.
Inconvenience between Argentina and Uruguay
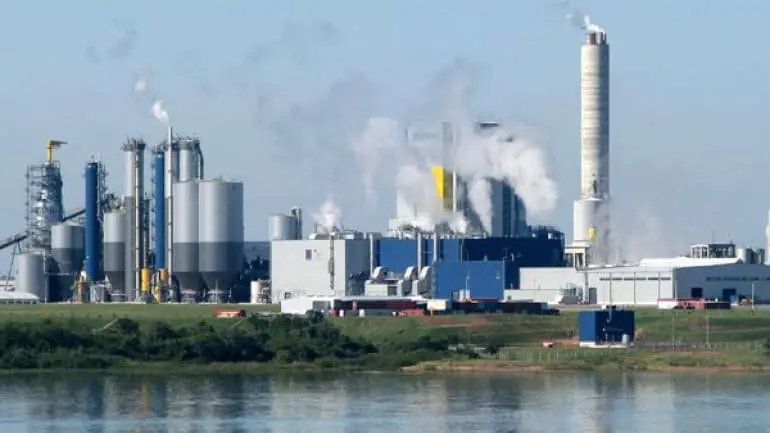
With regard to the Uruguay River, a few years ago, Uruguay decided to build a pulp mill on Uruguayan territory, which led to some conflicts between the two countries, as both had agreed that any action to be taken should be discussed at a meeting organised by the governments in power.
The mill was to be built near Uruguay’s international waters, in the towns of Fray Bentos in Uruguay and Gualeguaychu in Argentina.
This caused great diplomatic confrontations that were difficult to resolve, thanks to which both countries called for different opinions from ambassadors, of course with the help of a mediator, this mediator was the King of Spain.
After many talks and many problems, the problem was solved by the International Court of Justice, which put an end to the environmental protests that had arisen and took the name of Gualeguaychu.
Later, on 13 October, the problem began when the President of Uruguay, José Mujica, decided to approve a 10% increase in pulp production at UPM’s Fray Bentos mill. The Uruguayan president wanted to increase the mill’s production by 1.1 million tonnes per year. As a result, Argentina decided to sue the Uruguayan government again for acting without being consulted.
The case was brought before the International Court of Justice in The Hague on the basis of the Uruguay Treaty. This treaty stipulates that any movement or information on the Uruguay River that is to be made in the waters of the river must be strictly consulted with the other side of the river, i.e. the other government, and the Uruguayan government was in breach of this law.
Uruguay River: Map
Here we show you the route of the tributary through the country and its mouth. In this way, you will be able to see all the information we mentioned before, its length, flow and other data of this fantastic river.
Current situation of the Uruguay River
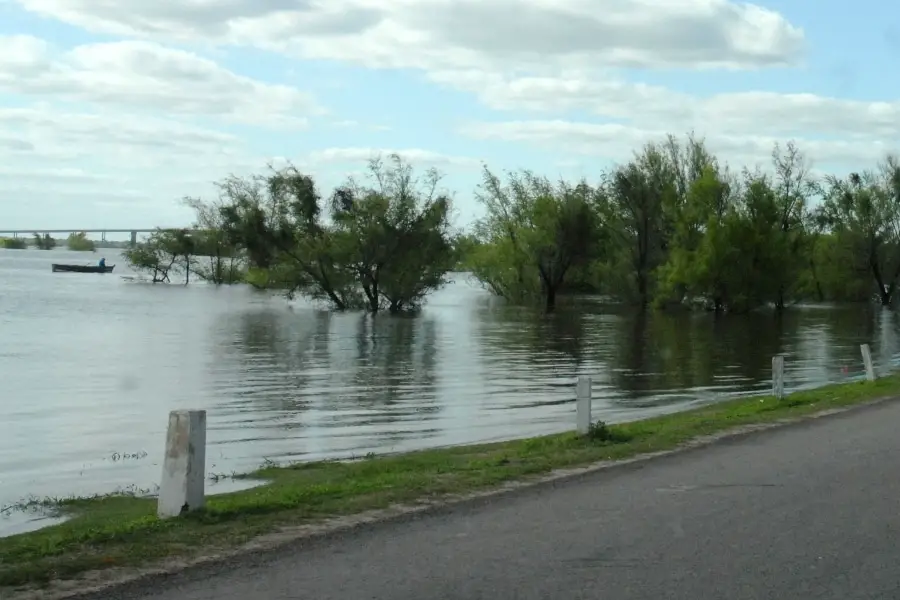
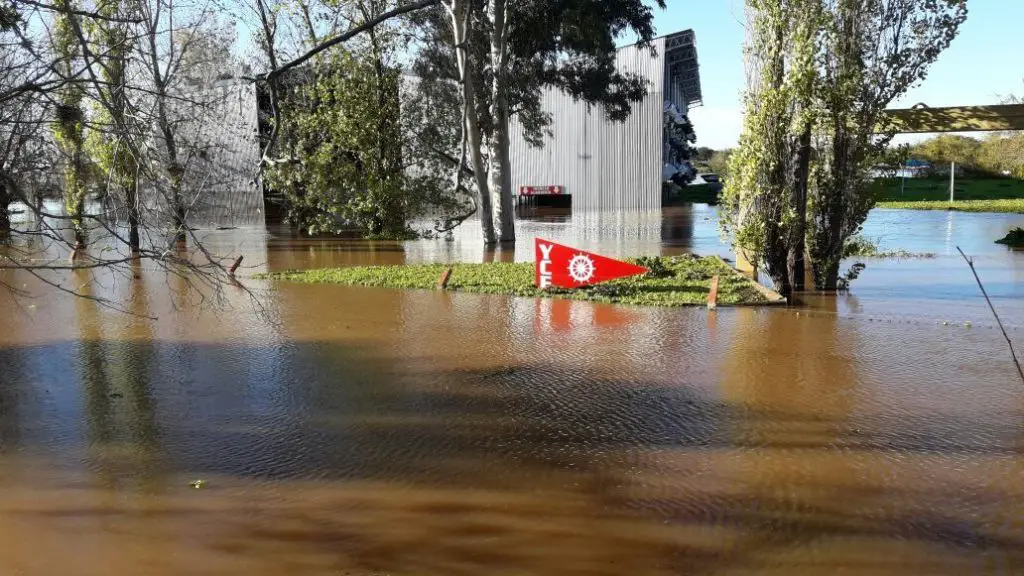
At the moment there are heavy rains that have caused the flow of the Uruguay River to reach almost 15 metres high in the big city of Concordia, this has made the families living in the city take precautions so that many will be urgently evacuated in case of a natural disaster that completely destroys each house. These rains make the weather very similar to that of the Mississippi.
Specialists from the hydrological department of the Joint Technical Commission, or CTM for short, pointed out that the situation could be a little more serious, with the water level at Salto Grande reaching 32.23 metres. So far, the normal level of the Uruguay River at Colón is 14.6 metres, although it is still rising, and it is estimated that in the next few weeks it could reach 14.50 metres and then the 15 metres that everyone fears.
The authorities have also said that the sites will be given to people who have not been fully affected by the fast-moving waters caused by the rains. The flow closest to the dam has been around 24,700 m3/s and the flows that have been evacuated to avoid major problems will increase to around 25,100 m3/s. The normal level of the Uruguay River at Colon and the major ports will rise, and Concordia will remain at around 14.30 m.
After all this, the authorities said that the knowledge of rainfall and precipitation, the height of the flows could gradually increase and the river could reach very high levels, not exceeding 15.20 metres in the city of Concordia. In addition, 11,000 people have been evacuated from the province of Entre Rios due to the heavy flooding of the Uruguay River.
Unfortunately, the end product of the heavy rains that have brought so much water is anything but peaceful for the people who live along the Uruguay River. During one of the floods, the volume of water that rose and fell for three days in a row brought with it a lot of rubbish that polluted the harbours and banks.
The local authorities took it upon themselves to clean up the mess, and also to heal the trees that had fallen victim to so much turmoil. An alarming number of dead animals were found that could not withstand the tides and heavy rains that hit the coast, including the belongings of the villagers, which were taken to a centre to be removed as many of these people were left with virtually nothing.
In conclusion, we can say that this river is also one of the most important rivers in South America, for the simple reason that it has the necessary characteristics to be included in this list. Thanks to its simplicity, beauty, unique atmosphere and the love of its people, the Uruguay River has become one of the best rivers for fishing and family recreation.