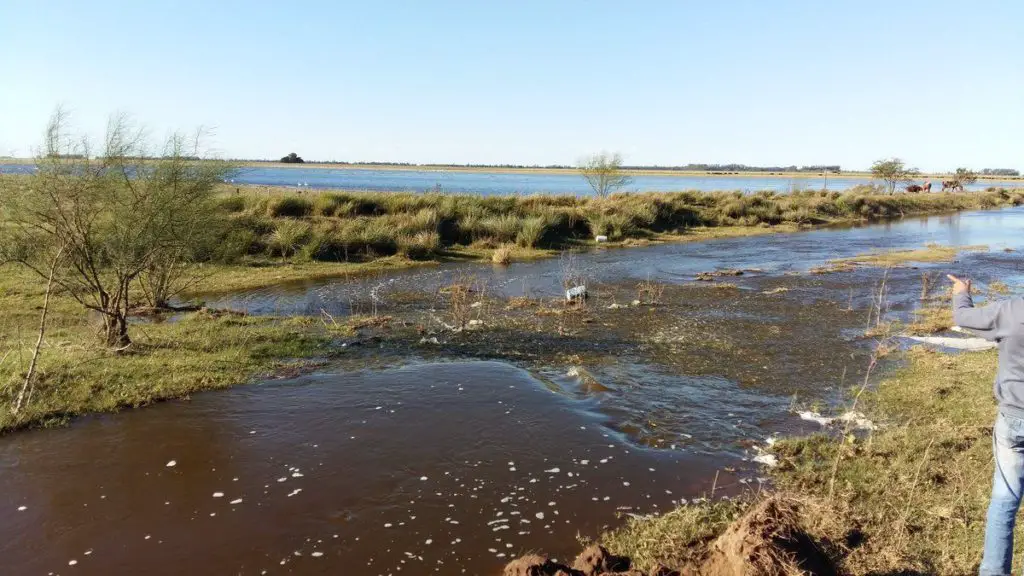
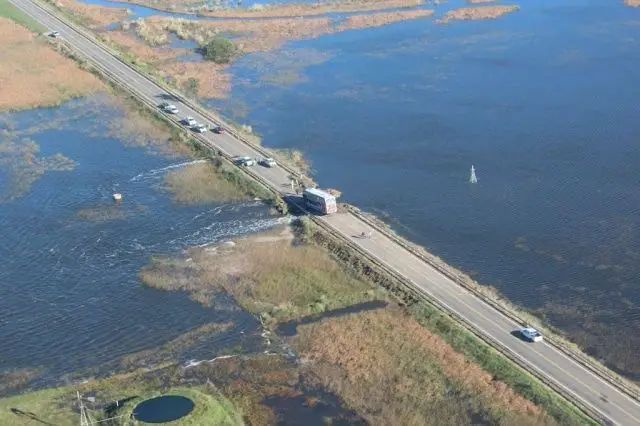
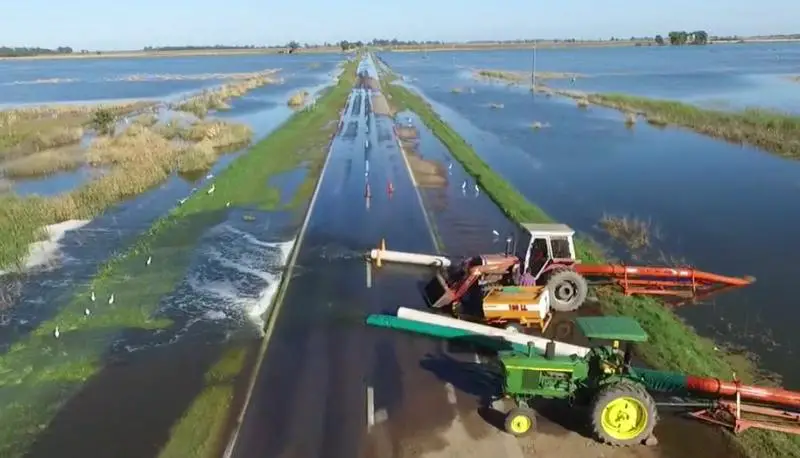
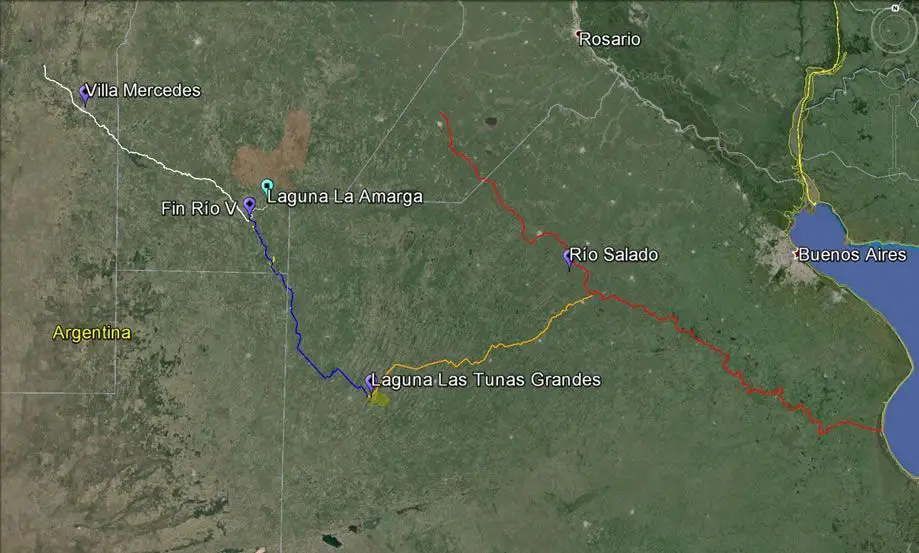
During the rainy season, the waters of the Quinto sometimes rise high enough to reach the provinces of Santa Fe and Buenos Aires, and sometimes even the Salado River basin. The length of the Quinto River depends on the season.
It can vary from 375 kilometres (233 miles) in the dry season to 878 kilometres (546 miles) after heavy rains (see article: Snake River).
Indice De Contenido
Río Quinta history
The presence of man in the Río Quinto area dates back 8500 years, or 6500 BC, in the Inti Huasi caves. B.C., in the caves of Inti Huasi (from the Quechua language, meaning “House of the Sun”), which testifies to the presence of tribal groups in the area of San Luis.
It seems that these groups disappeared, only to reappear 300 years later, in 5900 BC, when the area had acquired its present characteristics, to devote themselves to hunting and gathering fruit, such as carob trees.
From then on, life in the San Luis area changed and was restricted to the slopes of the mountain range. The best places for hunting in the summer were the highlands, while fruit gathering took place along the banks of the great rivers and in the lowlands, especially in the Conlara valley.
When indigenous groups arrived from southern Peru in 2000 B.C., bringing land for agriculture and cattle raising, the human groups were no longer able to make their temporary migrations according to the climate of each season and began to look for intermediate areas to settle.
Map of the Quinto River
The Quinto River, also known as the Popopis River, is located in central Argentina. It rises in the Sierra de San Luis, near Mount Retama, in the province of San Luis. The Quinto flows southeast (see article: Rio Solimoes).
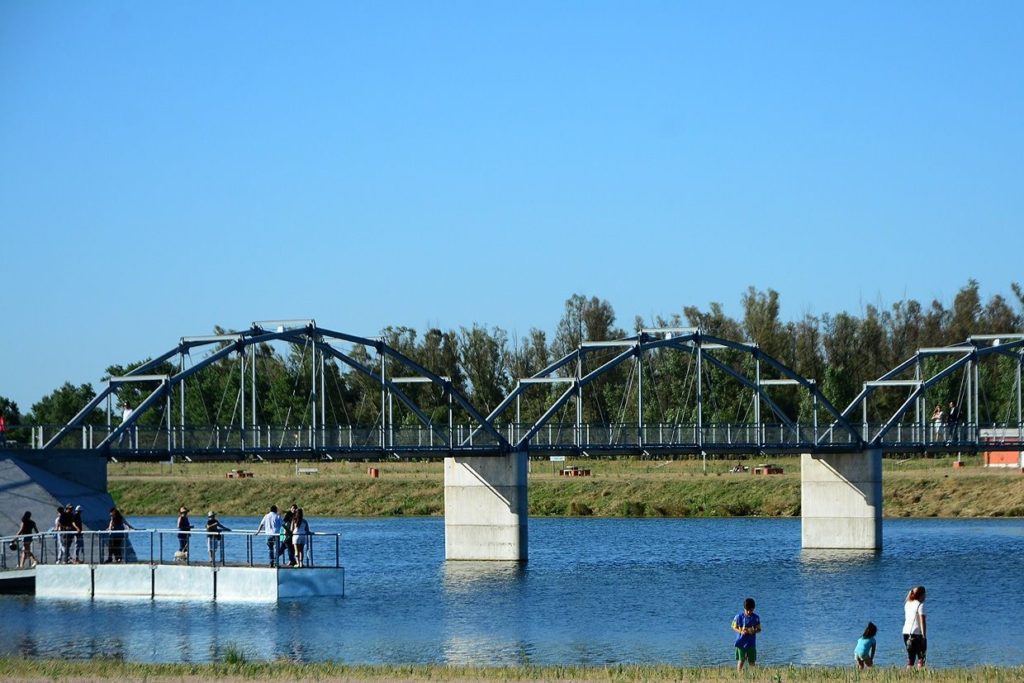
Near the Paso de las Carreteras dam, the Quinto begins to flow through the pampas. It passes through the town of Villa Mercedes, where it is about 45 metres wide. It then flows through the province of Córdoba. Finally, in its lower course, it flows into the Bañados de la Amarga marshes.
Quinto River in Villa Mercedes
Villa Mercedes is a town in the province of San Luis, Argentina. It is located in the east-central part of the province, on the left bank of the Quinto River, 32 km from the border with Córdoba, on National Route 148 and near the intersection of National Routes 8 and 7.
National Route 7 connects the town with the provincial capital, San Luis, 90 km to the northwest. At the 2001 census, the population was 96,781 (see article: Río Putumayo).
The town was founded by Governor Justo Daract on 1 December 1856 as a Constitucional Fort, a mixed civil and military fortress, to protect the area from the attacks of the Ranquel Indians. The original name was changed to Villa Mercedes in 1861 by the inhabitants, who adopted the Virgen de las Mercedes as their patron saint.
The line from Villa Mercedes to Mendoza was to become a stop on the route from Buenos Aires to the Chilean border and was purchased by the Great Western Railway of Argentina in 1887, later becoming part of the Buenos Aires and Pacific Railway network.
Villa Mercedes was officially declared a town in 1896. It is now the second largest in San Luis and an industrial and educational centre, housing a branch of the National University of San Luis (see article: Río Ohio).
Geography of the Quinto River
The Quinto River has an area of 75.2 square kilometres (29.0 sq mi) as of 1997. Of this area, 4.07 km2 (1.57 sq mi), or 5.4%, is used for agricultural purposes, while 20.29 km2 (7.83 sq mi), or 27.0%, is forested.
Of the remaining land, 1.92 km2 (0.74 sq mi) or 2.6% is developed (buildings or roads), 2.72 km2 (1.05 sq mi) or 3.6% is rivers or lakes and 27.84 km2 (10.75 sq mi) or 37.0% is unproductive land. Of the built-up area, 0.7% was used for housing and buildings and 1.6% for transport infrastructure.
Outside wooded areas, 22.0% of the total land area is covered by forest and 1.7% by orchards or small groups of trees. Of the agricultural land, 4.7% is used for crops. Of the water in the municipality, 3.0% is in lakes and 0.7% in rivers and streams. Of the unproductive land, 20.5% is unproductive vegetation and 16.5% is too rocky for vegetation.
The municipality is located in the district of San Luis, on both sides of the upper valley. Its boundaries extend from the peaks above the valley, at an altitude of over 2,800 m, to the valley at 1,011 m. It is made up of the village of Quinto and the hamlets of Altanca, Ambrì, Catto, Deggio, Piotta and Varenzo.