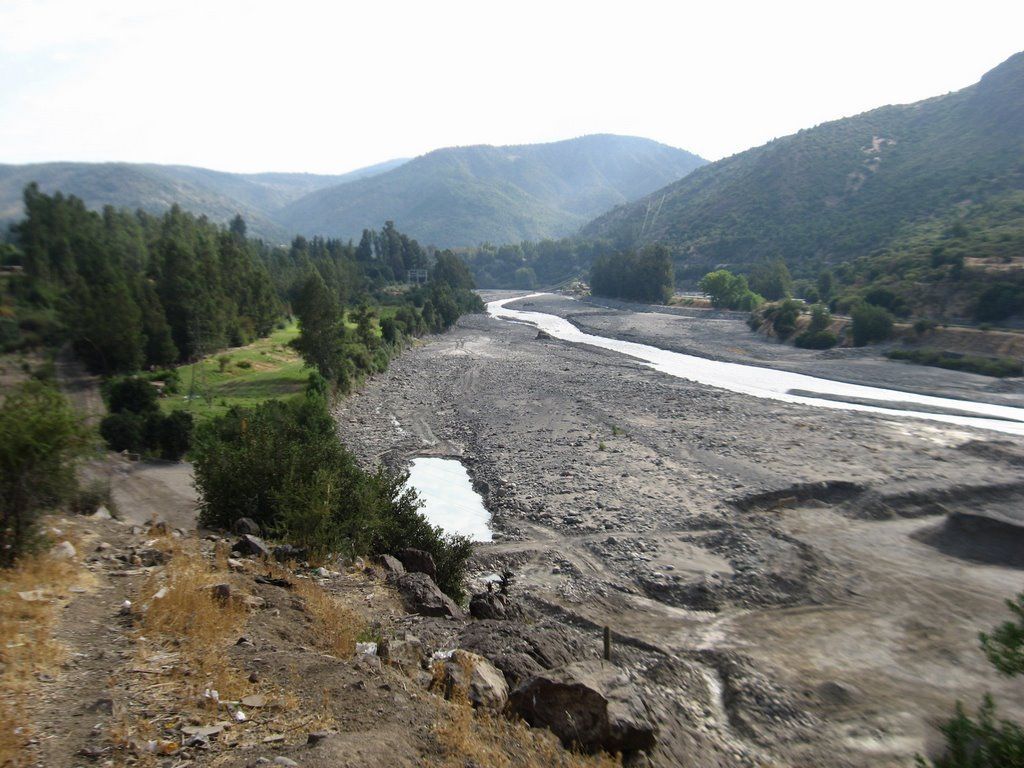
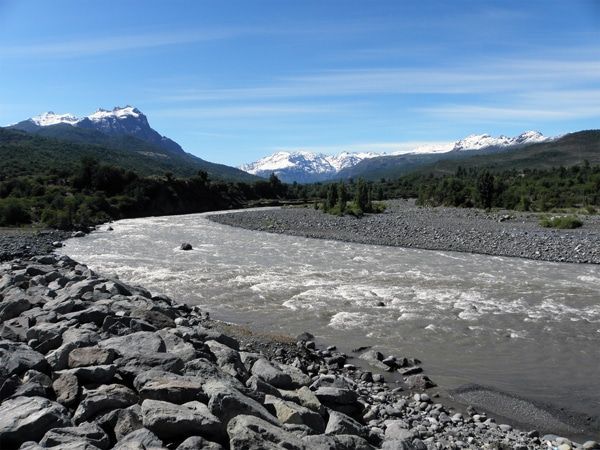
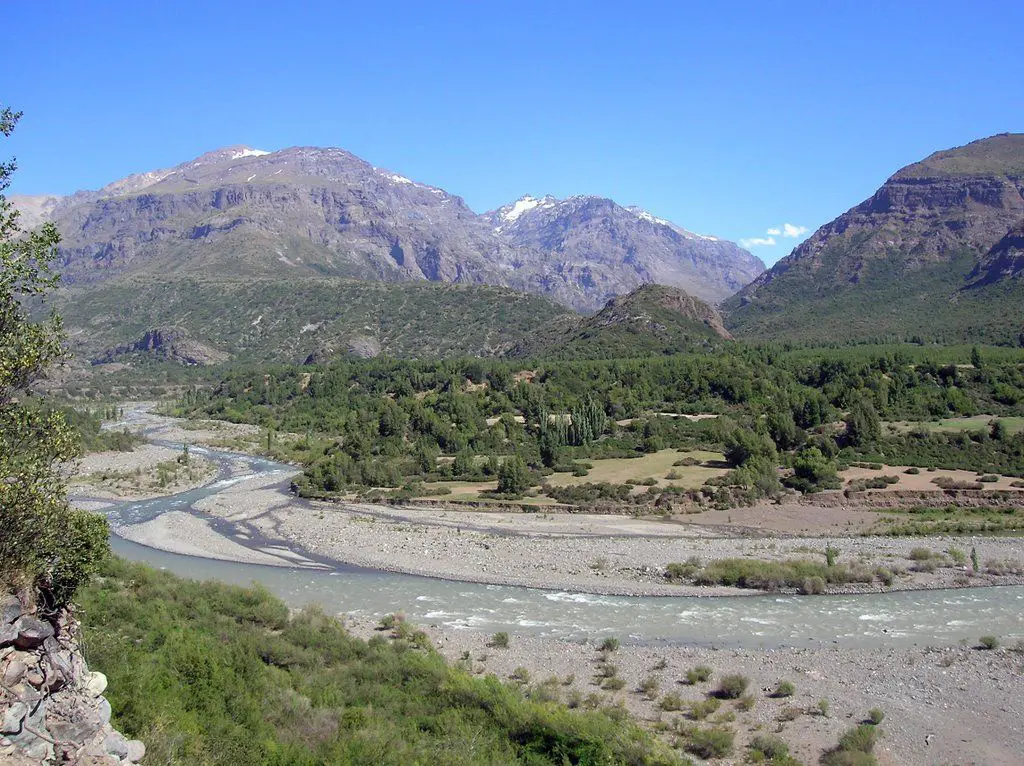
The Cachapoal River is a tributary of the Rapel River in Chile, located in the area of General Libertador Bernardo O’Higgins. The river shares its name with the town of Cachapoal. The valley is named after the Cachapoal River, which flows through the Rapel Valley, along with the Claro and Cortaderal Rivers.
Indice De Contenido
Features of the Cachapoal River
The Cachapoal River is located in the O’Higgins Region, Region VI of the Republic of Chile. The Cachapoal is not generally known as a whitewater river, except for the small section of Class II / III whitewater between Termas de Cauquenes and Sauzal (see article: Río Cautín).
Most of the Cachapoal River is devoted to heavy industry and power generation. On its northern banks, east of the city of Rancagua, is the world’s largest underground copper mine, called “El Teniente”, owned by the Codelco Corporation.
The main dam on the river is located in Coya, near the confluence with the Coya River. The most important dam in the region is on the Pangal River, a tributary of the Cachapoal River upstream (see article: Río Elqui).
These dams were built in 1911 and 1921 to supply electricity and water to the copper mine. In 2004, they were sold to Pacific Hydro of Australia, along with all the water rights on the Cachapoal River. Pacific Hydro plans to develop the Cachapoal River, despite the environmental disaster it has caused on the Tinguiririca River to the south.
The stretch of river between these two dams is often dry due to water being diverted for power generation and copper mining. However, if discovered in good time, it is reported to be a good class IV/V for about 6 miles (10 km).
Map of the Cachapoal River
All these rivers flow into Lake Rapel. The climate of the valley is temperate and generally Mediterranean, protected by the coastal mountain range from the cooling influences of the Pacific Ocean (see article: Silala River).
Cachapoal River Basin
The Cachapoal Forest covers the municipalities of Las Cabras, Doñihue and Coltauco, with an area of approximately 105,000 hectares and a total population of 57,683 inhabitants, on land bounded to the south by the Cachapoal River and to the north by the peaks of the Metropolitan Region’s coastal mountain range.
The area has a temperate climate with a long dry season, with Mediterranean characteristics and wide temperature variations between the coldest and hottest months. In general, rainfall does not exceed 40 mm in seven months, which is enhanced by the climatic shielding effect of the coastal mountain range, which makes the sky less cloudy than along the coast.
The flora and fauna found in the area are protected thanks to the presence of two units: the Reserva Nacional Roblería del Cobre de Loncha and the Las Palmas de Cocalán National Park (private); although the latter was declared a National Park in 1971, the presence of private property made it impossible to enforce the decree, although it remains in force today.
Economy of the Cachapoal
The area covered by the CMF can be divided according to land use, with 29% for agriculture, 25% for native forest and 37% for grassland and scrubland, plus 1.6% for timber plantations (see article: Río Andalién).
Since the colonial conquest, extensive use has been made of natural resources, such as cereal cultivation, cattle breeding, the harvesting of trees for firewood and charcoal, and the collection of fallen leaves from the forest floor, all of which have contributed over time to the degradation and destruction of the natural resources of this territory, causing soil erosion and fragility.
Production is concentrated in the forestry and fisheries, manufacturing and mining sectors, which account for 67% of the regional GDP, of which 21% comes from forestry and agricultural fisheries. In recent years there has been a decline in the agro-fishery component, offset by an increase in forestry (from 29,000 to 361,000 hectares).
At the same time, the country is experiencing serious problems of inequality and injustice among the population, a situation reflected in the Human Development Index (HDI) for the participating communities, which shows a decline in contrast to the improvement in the quality of life of the inhabitants.